
Breakthrough in Marine Conservation: AI Outpaces Humans in Detecting Fish Sounds!
2025-03-13
Author: Daniel
Introduction
In a remarkable advancement for marine research, scientists have developed a neural network that can analyze underwater soundscapes on coral reefs at astonishing speeds—up to 25 times faster than human experts. This groundbreaking progress could revolutionize how we monitor and understand the delicate ecosystems of coral reefs, which are increasingly threatened by climate change and human activities.
Importance of Coral Reefs
Coral reefs are home to about 25% of all marine species, despite comprising less than 1% of the ocean's total area. These vibrant ecosystems are vital not only for marine life but also for coastal protection and fisheries. However, tracking the diverse and ever-changing populations found within coral reefs has proven to be a challenging task for researchers.
Traditional Monitoring Methods
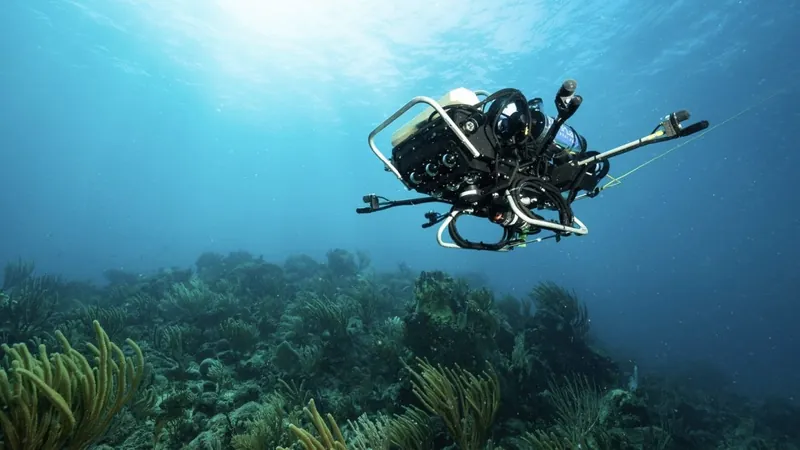
For years, marine biologists relied on passive acoustic monitoring, deploying underwater recorders to gather audio data from these ecosystems. Traditionally, analyzing this data required tedious manual work, which could take years to yield meaningful insights. Seth McCammon, an assistant scientist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and part of the research team, described the process as “awful” and “incredibly tedious.”
The AI Breakthrough
To address this pressing challenge, the WHOI team trained a sophisticated neural network capable of identifying and sorting through vast amounts of acoustic data in real time. According to their recent study published in the Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, this innovative algorithm not only matches the precision of seasoned experts but does so at a breakneck speed.
Future Applications of the Technology
With this advancement, the researchers envision a future where the technology can be integrated with various devices. For example, their co-author, Aran Mooney, is exploring the potential of deploying the neural network on a floating mooring that provides real-time updates on fish call counts. Additionally, they are working on equipping autonomous underwater vehicles like CUREE to actively listen for fish sounds and detect areas of significant biological activity.
The Holy Grail of Acoustic Research
This AI technology promises a solution to a long-standing problem in marine studies: linking distinct fish sounds to specific species. McCammon referred to the ability to match calls to species as the "holy grail" of acoustic research, a feat that would allow for real-time fish population monitoring and timely responses to ecological threats.
Transformative Implications for Conservation
The implications of this technology are transformative for conservation efforts. By enabling real-time identification of fish and their populations, researchers can better understand the health of coral reef systems and take proactive measures to preserve them, particularly in this critical era when reef environments are under siege.
Conclusion
As technology evolves, so too does our capacity to protect the world’s precious marine resources. The developments from the WHOI not only shine a light on innovative scientific approaches but also set the stage for a new era in marine conservation where timely and data-driven decisions become possible.
Stay tuned for the latest news in oceanographic innovations and how they could hold the key to preserving our planet's biodiversity.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)