Breakthrough in Head and Neck Cancer Treatment: How ctDNA Monitoring Could Change Survival Odds!
2025-08-22
Author: Ming
Head and Neck Cancer's Deadly Reality!
Recurrent and metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (R/M HNSCC) is notoriously aggressive, with only a small fraction of patients benefiting from current treatments. Traditional therapies often involve immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), occasionally paired with chemotherapy, yet the objective response rates leave much to be desired.
Game Changer: Pembrolizumab in the Spotlight!
Pembrolizumab has shown remarkable promise, particularly for patients with higher PD-L1 combined positive scores. Those with scores of 1 or higher enjoyed a median survival improvement from 10.3 to 12.3 months. But despite this, a staggering 66-95% of patients still fall short of significant improvement, pointing to an urgent need for new targeted therapies.
The Need for Dynamic Biomarkers!
The standard PD-L1 biomarker has proven to be a static measure — useful only at the start of treatment and not during ongoing therapy. What’s needed is a dynamic, non-invasive biomarker that continually reflects a patient's disease status, allowing doctors to tailor treatments in real-time.
Introducing ctDNA Monitoring!
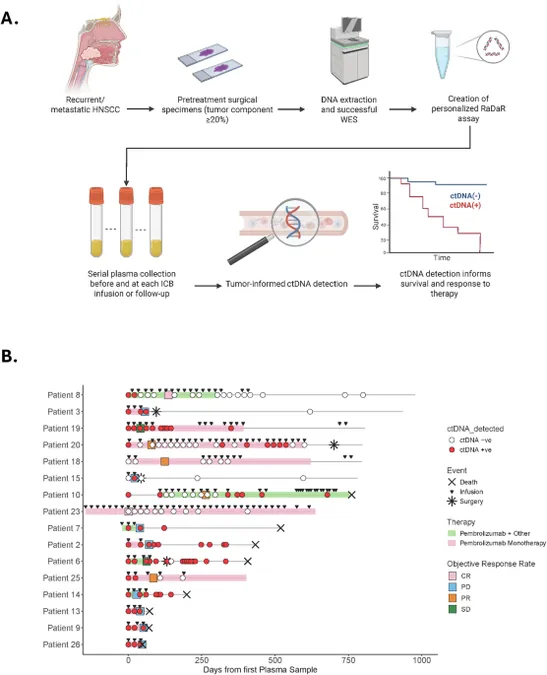
Enter ctDNA, a groundbreaking method that tracks circulating tumor DNA through liquid biopsies. This minimally invasive approach allows for real-time monitoring of treatment responses, significantly enhancing the clarity with which clinicians can tailor therapies for R/M HNSCC patients.
Early Results Are Promising!
A recent study from a single institution analyzed ctDNA dynamics across 137 blood samples from sixteen patients. They found that patients with undetectable ctDNA during treatment were significantly more likely to achieve improved overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). This indicates that monitoring ctDNA could directly inform treatment decisions.
The Implications Are Huge!
For example, when ctDNA was undetectable, patients enjoyed a much more favorable prognosis — three-year overall survival rates soared to 75%! This stands in stark contrast to those with detectable ctDNA, highlighting the profound impact this biomarker could have on patient management.
Spotting Trouble Early!
Furthermore, rising levels of ctDNA were linked to disease progression, suggesting that tracking this biomarker can alert doctors to potential issues long before they manifest in clinical evaluations.
What’s Next?
While these findings are exciting, it's imperative to conduct further prospective studies validating ctDNA's role. If proven effective, ctDNA monitoring could revolutionize treatment protocols, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate combination of therapies — potentially saving countless lives.
Conclusion: A New Dawn for R/M HNSCC!
The evolving landscape of head and neck cancer treatment highlights the potential for ctDNA monitoring as a game-changing tool. This pioneering approach may ultimately enhance survival rates and better manage patient care in the fight against R/M HNSCC!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)