Breakthrough in Bacteriophage Therapy: A Promising Weapon Against Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus faecalis
2025-08-28
Author: Wei
Phage ENP2309: A Game Changer in Infection Control
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have isolated a potent bacteriophage named ENP2309, demonstrating remarkable efficacy in combating infections caused by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis (VRE) in mice. This innovative approach to treating antibiotic-resistant infections offers hope in the ongoing battle against superbugs.
Innovative Isolation Techniques
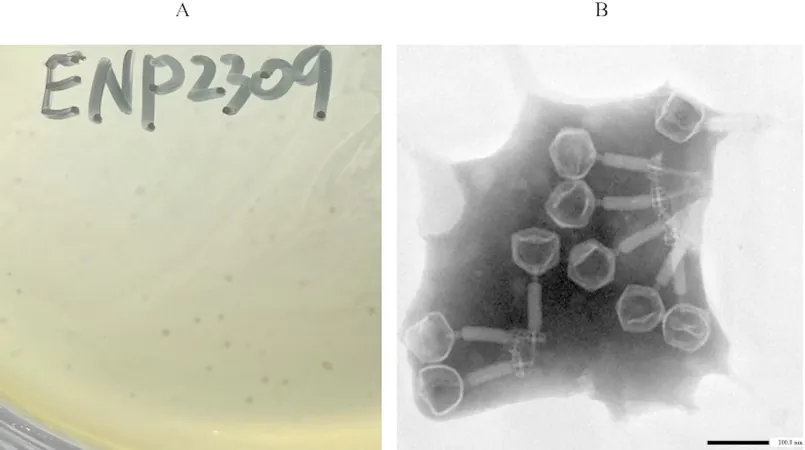
The research team utilized wastewater samples from yak farms in Xining, China, to isolate phage ENP2309. Following a meticulous purification process that involved the double-layer agar method and multiple rounds of isolation, the team secured a stable phage capable of targeting a broad spectrum of Enterococcus strains.
Unveiling the Science: Morphological and Biological Properties
Through advanced microscopy techniques, scientists observed that phage ENP2309 possesses an icosahedral head and a contractile tail. The phage showcased impressive therm stability, remaining infectious between 10°C and 60°C, while complete inactivity was noted above 70°C. It also thrived across a wide pH range, indicating its resilience in diverse environments.
Testing the Limits: Efficacy in Mice Models
In a controlled experiment, female BALB/C mice were separated into groups subjected to various treatments, including a direct challenge with E. faecalis. Notably, the treatment group that received phage ENP2309 showed zero mortality, contrasting sharply with the challenge group, which suffered 100% mortality within 96 hours. The phage's ability to restore health and prevent weight loss showcased its therapeutic potential.
Outcomes of Pathological Assessment
Detailed histopathological examinations revealed significant organ recovery among phage-treated mice, with nearly normal tissue architecture observed in the liver, spleen, and intestinal tracts. This starkly contrasted with the severe damage evident in untreated mice.
Understanding the Immune Response: Cytokine Profiling
Cytokine levels provide insights into the immune reaction against the E. faecalis infection. The treatment groups illustrated a quick restoration of immune balance, demonstrating ENP2309's dual potential: to act aggressively against pathogens while regulating the immune response.
Genomic Insights into Phage ENP2309
Sequencing revealed ENP2309's genome spans 148,806 base pairs with 153 predicted genes, highlighting its functional sophistication. This genome composition not only confirms its classification as a virulent phage but also suggests its substantial therapeutic capabilities against resistant bacterial strains.
Why Phage ENP2309 is a Beacon of Hope
As the global crisis of antimicrobial resistance continues to escalate, phage ENP2309 emerges as a beacon of hope. Its proven efficacy against VRE, coupled with a favorable safety profile, positions it at the forefront of future treatment strategies. Given the urgent need for effective alternatives to traditional antibiotics, further investigations of phage therapy are imperative, including studies on combination therapies to prevent bacterial resistance.
The Future of Phage Therapy: A New Era?
With the potential for widespread applications, including antimicrobial treatments and food safety measures, phage therapy represents a multifaceted approach to healthcare challenges. As researchers continue to explore and expand the possibilities of phage use, the future may hold innovative solutions and breakthroughs in managing resistant infections.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)