Breakthrough Discovery: Targeting Key Enzyme Could Revolutionize Cancer Immunotherapy
2025-01-17
Author: Siti
Introduction
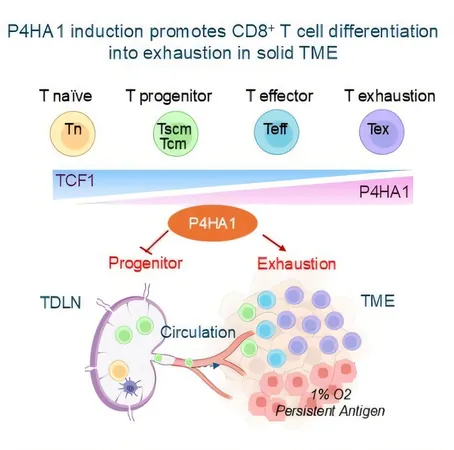
In a groundbreaking study, scientists at the A*STAR Genome Institute of Singapore (A*STAR GIS) have identified a pivotal enzyme, P4HA1 prolyl hydroxylase, as a potential game-changer in cancer immunotherapy. Found to be significantly upregulated in CD8+ T cells—the primary immune warriors against cancer—this discovery sheds light on how inhibiting P4HA1 could reinvigorate the immune response in patients with solid tumors.
Mechanism of Action
P4HA1 disrupts cellular energy production, leading to weakened immune cells that struggle to combat tumors effectively. Researchers have shown that by using small molecule inhibitors to target P4HA1, they can restore healthy immune functions, promote long-lasting immune memory, and help shrink tumors while preventing relapses. Remarkably, the inhibition of this enzyme has exhibited substantial effectiveness in combating immune-resistant tumors in mouse models.
Implications for Cancer Therapy
The implications of this research extend to enhancing existing cancer therapies, notably CAR-T cell therapy. By targeting P4HA1, modified CAR-T cells could become more potent, potentially increasing their effectiveness in eradicating cancerous cells. The findings of this study are set to be published in Cancer Cell in December 2024.
Biomarker Potential
Additionally, researchers discovered that higher levels of P4HA1 in blood immune cells are linked to cancer progression and relapse, making it not only a viable target for boosting immune response but also a potential biomarker for tracking tumor recurrence and the effectiveness of immunotherapies.
Selectivity and Challenges
While numerous metabolic and epigenetic regulators influence T cell function, they often present challenges in targeted therapies. P4HA1, however, is expressed minimally in naïve and memory T cells but surges during T cell activation, becoming more prevalent in exhausted T cells within the tumor microenvironment (TME). This selectivity positions P4HA1 as a unique target for developing specialized anti-cancer treatments.
Importance of Immune Response
The research underscores the importance of a robust systemic immune response to effectively fight cancer. By examining tumor-draining lymph nodes (TDLNs) and peripheral blood, the study highlights how targeting P4HA1 in immune cells can enhance and maintain long-term immune responses, resulting in sustained tumor control and better therapeutic outcomes.
Expert Opinions
Prof. Yu Qiang, the Senior Group Leader of the Laboratory of Precision Cancer Medicine at A*STAR GIS, expressed enthusiasm about this research, stating, "Our findings bridge the gap between fundamental science and clinical applications. We aim to develop optimized strategies targeting P4HA1, including innovative chemical inhibitors and advanced CAR-T cell therapies, to provide efficient treatment options for solid tumors."
Dr. Wan Yue, Executive Director of A*STAR GIS, emphasized, "The potential of P4HA1 as a biomarker for cancer progression and immunotherapy resistance could lead to more tailored monitoring and treatment strategies in the future, enhancing immunotherapy effectiveness and ensuring better patient outcomes."
Conclusion
Stay tuned as this research unfolds, possibly heralding a new era in cancer treatment that could drastically improve survival rates and quality of life for patients globally!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)