Breakthrough Discovery: Key Gene Linked to Rice Leaf Growth and Soaring Methane Emissions
2024-11-14
Author: Jia
Introduction
In a groundbreaking study, researchers have illuminated the vital role of rice leaf veins, which are essential for the plant's growth and health. These structures not only support the leaves but are also crucial for transporting water, gases, and nutrients throughout the plant.
A team led by Dr. Wu Yuejin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science under the Chinese Academy of Sciences has unveiled a pivotal gene that influences the development of these veins and has significant implications for methane emissions from rice cultivation, as detailed in their recent publication in *Plant Science*.
Methodology
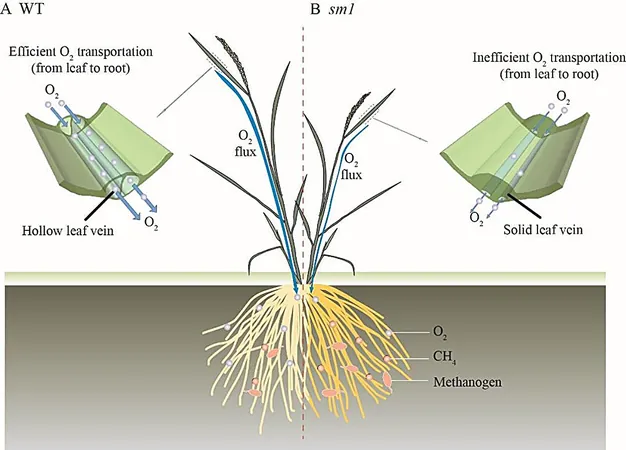
Utilizing advanced ion beam mutagenesis technology, the research team identified a unique rice mutant characterized by solid rather than hollow leaf veins. This mutation resulted in shorter plants with a shocking 49% reduction in dry weight compared to their normal counterparts.
Findings
Further analysis revealed that this mutant was linked to a gene dubbed SM1, which plays a seminal role in the formation of rice leaf veins. The SM1 gene encodes a "litter zipper" protein that interacts specifically with another protein named OSHB1, which helps regulate the expression of OSH1—this gene is crucial for the development of the plant's stem cells and vascular system.
Such interactions dictate how effectively the rice plant can develop its vascular network, a factor fundamental to its growth.
Impact on Methane Emissions
Interestingly, the researchers observed that in mutants exhibiting solid leaf veins, these structures were filled with varied cell types. This abnormal configuration significantly hindered the plant's ability to transport oxygen to its roots, leading to increased methanogenic activity in the surrounding rhizosphere.
The result? A staggering 96.8% surge in total methane emissions, a greenhouse gas that poses serious environmental concerns.
Conclusion
The implications of this study are enormous. As rice is a staple food for millions worldwide, understanding the genetic factors that influence both plant growth and greenhouse gas emissions is crucial.
This discovery could pave the way for developing rice varieties that not only improve yields but also mitigate methane emissions, significantly impacting agriculture and climate change mitigation strategies. In a world grappling with food security and environmental challenges, findings like these could be a game-changer—stay tuned for more on this important research!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)