Breakthrough Discovery: Focal Adhesion Kinase Variants Linked to Neuroendocrine Tumors in Pancreas and Breast
2025-09-17
Author: Mei
A Major Leap in Cancer Research!
In a groundbreaking study, researchers from the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College have unveiled shocking findings regarding the oncogene Focal Adhesion Kinase (FAK) and its connection to neuroendocrine tumors (NENs) of the pancreas and breast. Published in Frontiers of Medicine, this study could reshape our understanding of these complex cancers.
Understanding Neuroendocrine Neoplasms (NENs)!
Neuroendocrine neoplasms are a diverse group of tumors arising in various organs. One of the pivotal challenges in treating these cancers has been identifying their unique genetic footprints. This research provides a vital clue by revealing high frequencies of specific FAK splicing variants.
Key Findings: The Role of FAK6/7!
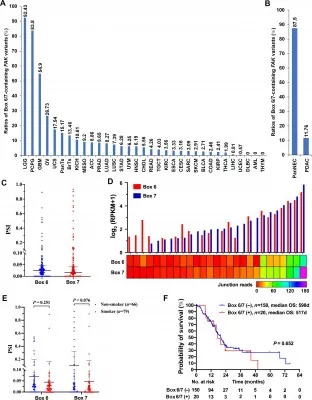
Analyzing data from The Cancer Genome Atlas involving 9,193 patients with 33 cancer types, the researchers discovered Box 6/Box 7-containing FAK variants (FAK6/7) predominantly in neuroendocrine tumors. Astonishingly, 87.5% of pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinomas and a significant portion of breast neuroendocrine carcinomas exhibited these variants, while they were largely absent in other cancer types.
Significance for Pancreatic and Breast Cancers!
In the study's examination of 157 tumor samples from Chinese patients, 75.6% of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors were positive for FAK6/7, alongside high positivity rates in pancreatic solid pseudopapillary neoplasms. In stark contrast, non-neuroendocrine breast cancers showed no signs of these variants, highlighting their potential as a distinguishing biomarker.
The Mechanism Behind the Discovery!
Delving deeper, the researchers uncovered that a splicing factor known as serine/arginine repetitive matrix protein 4 (SRRM4) is overexpressed in tumors that are FAK6/7 positive. This overexpression seems to promote the formation of these specific genetic variants, paving the way for further exploration into targeted therapies.
A New Hope for Treatment!
The implications of these findings are immense. Not only could FAK6/7 serve as a powerful biomarker for diagnosing neuroendocrine tumors, but it may also emerge as a crucial target for future therapeutic strategies. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of these orphan diseases, FAK6/7 stands out as a beacon of hope for improved treatments and patient outcomes.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)