Breaking News: SORL1's Crucial Role in Alzheimer's Unveiled!
2025-01-17
Author: Li
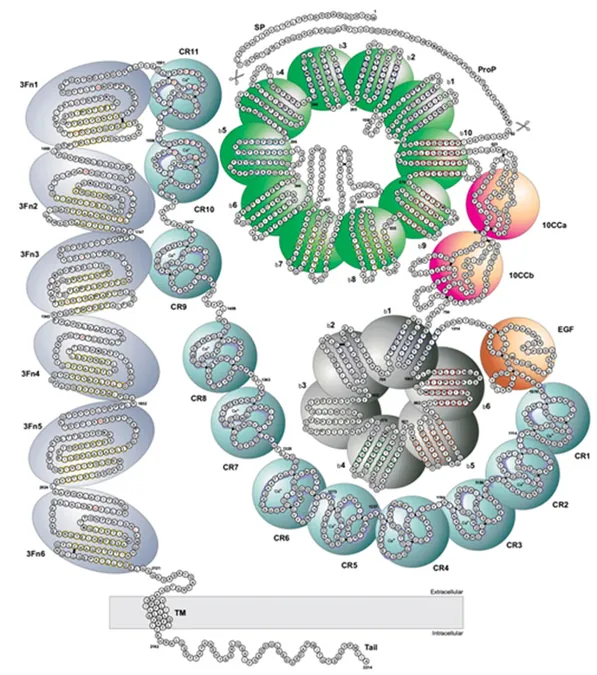
Recent research has shed new light on the essential functions of the sorting receptor SORL1 in the context of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), positioning it alongside other key genetic players in the disease's development. As scientists recognize SORL1's significance more than ever, a detailed exploration of its role in neuronal and microglial function has revealed vital insights into how mutations can disrupt its critical trafficking abilities, thereby exacerbating neurodegenerative processes.
SORL1 operates in tandem with the retromer complex, facilitating the transportation of vital protein cargoes within the endolysosomal system—an integral component of cellular recycling. Mutations that inhibit this trafficking are emerging as important factors in Alzheimer’s pathology, marking SORL1 as a key player in what is being dubbed the “causal quartet” of AD genes, which includes APP, PS1, and PS2. In 2023, an extensive mutation database launched by Alzforum cataloged approximately 500 mutations linked to SORL1, indicating the growing importance of understanding its genetic variants.
The Evolving Landscape of SORL1 Research
Fast forward to 18 months later, and we see a surge in studies focusing on SORL1 variants that have been linked to familial cases of AD. News has emerged of various pathogenic SORL1 mutations—including the Y1816C variant, which appears to cause autosomal-dominant AD, according to research led by Olav Andersen from Aarhus University. This particular mutation affects SORL1's dimerization process and impedes its interaction with the retromer complex, leading to compromised functionality and increased amyloid-beta production.
Meanwhile, the R953C variant showcases similar disruptive effects, inhibiting proper SORL1 folding and impeding its journey to the cell membrane. Despite only two variants showing links to familial AD, the potential for numerous other pathogenic variants remains, as much of the current genetic analysis continues to unfold.
Importantly, studies have also found that SORL1 variants exhibit different effects depending on human populations. Recent genome-wide association studies identified protective and risk factors related to SORL1 in both East Asian and European participants. A significant finding was the discovery of a protective haplotype present in East Asians, which appears to enhance cognitive function and protect against AD severity.
SORL1: The Double-Edged Sword in Neurons and Microglia
SORL1's influence is not confined to neurons alone; research highlights its equally vital role in microglia, where it supports lysosomal function. In microglia, deficiencies in SORL1 lead to impaired lysosomal enzyme function, preventing proper degradation of harmful substrates, including amyloid-beta plaques. When SORL1 is muted, while microglia may engulf more amyloid-beta, they struggle to respond to inflammation, which could worsen neurodegenerative processes.
The differential role of SORL1 in these cell types underscores the intricacies of AD pathology. While in neurons its absence contributes to amyloidogenesis, in microglia, it’s a failed recycling system leading to neuroinflammation. The specific mechanisms by which SORL1 mutations thwart protective functions are now the focus of extensive studies.
Future Directions: Biomarkers and Therapeutic Approaches
For researchers, the next target is establishing a reliable biomarker for SORL1 function. Preliminary studies indicate that levels of soluble SORL1 in cerebrospinal fluid could hold the key to identifying SORL1-related neurodegeneration. As ongoing research continues, this could pave the way for both preventative strategies and targeted therapies aimed at improving neuronal health and microglial function within the Alzheimer’s landscape.
It's clear: understanding the complexities of SORL1 is critical not just for unraveling the mystery of Alzheimer's, but for crafting a future where effective interventions provide hope for those at risk of this debilitating disease. Stay tuned as this scientific journey unfolds and potentially opens new doors in Alzheimer's treatment and prevention!
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)