Breaking Down the Ocean's Carbon Secrets: New High-Resolution Mapping Reveals Hidden Details
2025-06-25
Author: Daniel
As the world grapples with soaring carbon dioxide levels, the ocean's crucial role in countering human-caused climate change continues to shine. Shockingly, the ocean retains approximately 25% of all the carbon dioxide emitted by human activities.
Yet, this carbon absorption isn't consistent across the vast marine landscapes. Enter a groundbreaking satellite-based mapping tool that delivers unprecedented details about the ocean carbon sink—a pivotal yet unpredictable aspect of our planet's climate system.
The Ocean's Role in Climate Regulation
Remarkably, the global ocean has buffered climate change by absorbing nearly 90% of excess heat and a quarter of the carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere from human activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels. This ‘sink’ helps mitigate global warming, but its impact does not come without consequences.
The absorption of carbon dioxide leads to declining seawater pH levels and disrupts the ocean's carbonate chemistry—contributing to a phenomenon known as ocean acidification. This troubling trend jeopardizes marine life and ecosystems worldwide.
Unlocking the Secrets of Ocean Dynamics
Understanding the intricate dynamics and fluctuations of ocean carbon sink processes is paramount for the health of our oceans and, consequently, our planet. While significant strides have been made in grasping seasonal and annual changes in the ocean carbon sink, short-term variations remain poorly understood.
Currently, most data sets used to study the ocean carbon sink come in at a sluggish resolution—about 100 kilometers and updated monthly. Such limited data fails to capture the rapid shifts that characterize ocean dynamics.
A Revolutionary Approach to Ocean Data
Nicolas Gruber from ETH Zurich reveals the challenge of improving these global datasets due to the sparse direct measurements of surface carbon dioxide across various regions. To combat this, his team creatively employed machine learning techniques to introduce a cutting-edge version of their OceanSODA-ETHZ product.
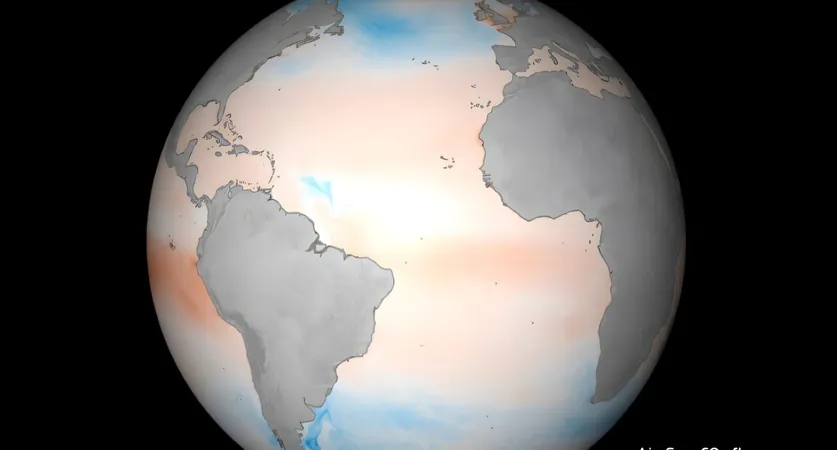
This innovative global dataset provides insights into surface ocean carbon dioxide and the carbonate system with an extraordinary resolution of 25 kilometers, updating every eight days—more than 30 times sharper than previous datasets. By integrating advanced satellite data, researchers can now interpolate measurements in both time and space.
Visualizing Ocean Carbon Exchange
The breakthroughs are vividly illustrated in animations showcasing carbon dioxide exchanges between the atmosphere and the ocean, revealing the impacts of various events such as hurricanes. Areas shaded blue represent carbon absorption, while red indicates carbon release back into the air, with arrows illustrating surface wind patterns.
Understanding the Impact of Extreme Events
At the recent ESA Living Planet Symposium, scientists discussed how this high-resolution dataset allows for deeper analysis of short-lived but intense ocean events. Professor Jamie Shutler from the University of Exeter highlighted how the dataset aids in differentiating the effects of hurricanes, which can churn up deep, carbon-rich waters to the surface—resulting in dramatic shifts in ocean carbon dioxide levels.
These insights present exciting new avenues for understanding oceanic carbon absorption and foresee how these processes may evolve amid ongoing climate change challenges.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)