Breaking Down the Links: Insulin Resistance and Urinary Incontinence in Non-Diabetic Women Explained!
2025-09-17
Author: Wei Ling
A Growing Health Concern for Women
Urinary incontinence (UI), especially urge urinary incontinence (UUI), has emerged as a pressing health issue among middle-aged and older women globally. This study dives deep into the correlation between insulin resistance (IR) and UUI in non-diabetic women, unveiling crucial connections.
Methodology: An In-Depth Analysis
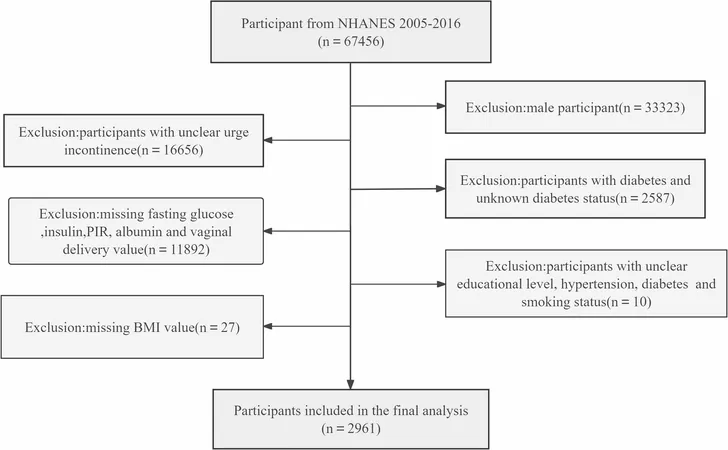
Utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) spanning 2005 to 2016, researchers assessed the link between IR and UUI among women aged 20 and over. Multiple logistic regression models were employed to analyze the relationship, alongside subgroup analyses and detailed curve fittings to ensure robustness in findings.
Key Findings: Obesity as a Major Player
Among 2,961 participants, a striking 28.20% reported experiencing UUI. Initial analysis indicated a significant positive correlation between insulin resistance levels (measured by HOMA-IR) and UUI prevalence, suggesting that for every unit increase in HOMA-IR, the risk of UUI rose by 3%. However, after adjusting for body mass index (BMI), this association diminished significantly, indicating that obesity plays a crucial role in mediating the relationship.
Obesity: The Underlying Culprit
The research underscores obesity as the primary modifiable risk factor for UUI among non-diabetic women. Weight management emerges as a pivotal strategy for reducing UI risk, highlighting the need for focused interventions on lifestyle and dietary changes.
Understanding the Impact of Insulin Resistance
While insulin resistance is commonly connected to various health issues, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, its direct link to UUI appears largely contingent upon obesity. As obesity leads to chronic low-grade inflammation and hormonal changes, it affects bladder function, elevating the risk for UI. Thus, targeting obesity could indirectly alleviate concerns arising from insulin resistance.
Recommendations for Women Everywhere
Given these findings, women should consider weight management as a fundamental component of their health strategy. Engaging in a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly mitigate the risks of urinary incontinence and enhance overall well-being.
Final Thoughts: A Call to Action
This study reaffirms the importance of analyzing weight in relation to urinary health, rather than focusing solely on metabolic issues like insulin resistance. By prioritizing weight loss, women can tackle the multifaceted challenges posed by urinary incontinence effectively.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)