Battle of the Bots: How Leading AI Models Measure Up in Kidney Imaging Recommendations
2025-07-04
Author: Nur
The Rise of AI in Medical Decision Making
Natural language processing (NLP) has rapidly evolved since its inception in the 1950s, transforming from primitive beginnings to powerful tools in modern medicine. Today, large language models (LLMs) such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT-4.0, Google’s Gemini, and Microsoft’s Copilot are playing a pivotal role in healthcare, aiding in various tasks from administrative duties to resolving complex medical inquiries. However, despite their potential, the consensus on their reliability remains incomplete.
Emergency Visits and the Imaging Dilemma
Flank pain due to urolithiasis (kidney stones) is a leading reason for emergency department (ED) visits, a trend that has surged in recent years. Current guidelines advocate the use of Non-contrast Enhanced CT (NCCT) following initial ultrasounds to confirm kidney stones. Yet, ambiguities about when imaging is truly necessary complicate clinical decision-making for ED practitioners.
A Gap in Research on AI's Role in Imaging Recommendations
Despite widespread usage of LLMs, there's a shocking lack of research on how they determine the most suitable imaging techniques for kidney stone patients. This study sets out to address this gap, specifically evaluating whether the recommendations from ChatGPT-4.0, Gemini, and Copilot align with established expert consensus when faced with 29 detailed clinical scenarios.
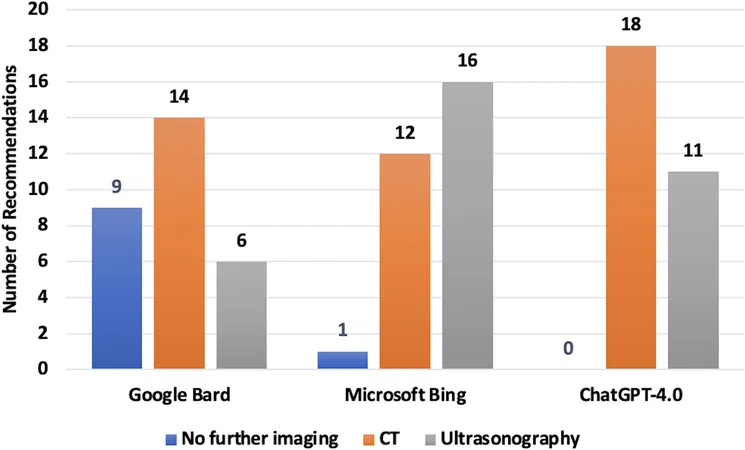
Methodology: How AI Models Were Tested
Between March and April 2024, the three LLMs were confronted with 29 different clinical vignettes focused on acute flank pain. Each model was tasked with prescribing the best imaging strategy: no further imaging, ultrasound, or various types of CT scans. Responses were analysed for consistency with established consensus, with categories including perfect, excellent, and moderate agreement levels.
What the Findings Reveal About AI Models
The results were revealing: Gemini consistently demonstrated superior alignment with expert opinions compared to ChatGPT-4.0 and Copilot. Notably, Gemini achieved an impressive agreement rate of 82.7%, suggesting its potential as a reliable tool for clinicians faced with tough imaging decisions.
Evaluating AI's Evolving Role in Clinical Decisions
The study highlights growing interest in how LLMs can enhance clinical decision-making. Past studies suggest varying levels of effectiveness among these models, with Gemini often lagging behind in other contexts—revealing a complicated landscape where performance varies based on the specific clinical inquiry.
Navigating Ethics and Legalities of AI in Healthcare
As AI becomes more integrated into healthcare, ethical and legal implications come to the forefront. Providers must trust the decision-making logic of these systems to maintain patient confidence and address accountability concerns when errors occur. Furthermore, stringent data protection laws, like HIPAA in the U.S. and KVKK in Turkey, must be adhered to, ensuring patient data security.
Limitations and Future Directions
This study isn't without limitations: variations in question phrasing, the limited scope of clinical scenarios, and the lack of a power analysis could influence findings. However, its structured methodology lays the groundwork for further exploration into LLMs' roles in healthcare. Future research can refine these models, improving their reliability and alignment with expert medical guidelines.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)