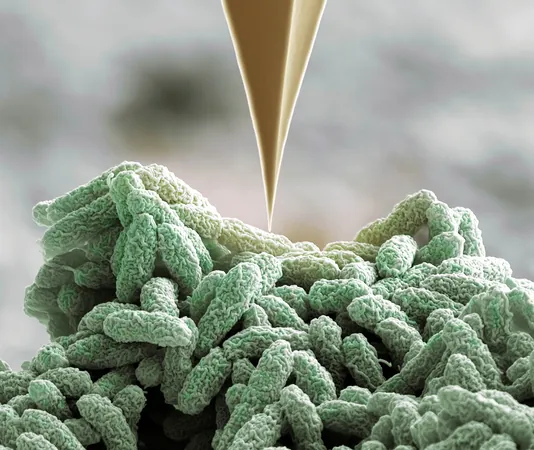
Bacteria Unleash Tiny 'Nano-Spearguns' in a Microbial Arms Race
2025-03-12
Author: John Tan
The Mechanism of Nano-Spearguns
T6SS acts as an intricate injection mechanism that enables bacteria to shoot toxic proteins directly into competing microbes or even host cells. This remarkable defense strategy has been likened to a microscopic harpoon gun that can inflict damage on enemies and alter microbial communities within various environments such as soil, aquatic ecosystems, and the human gut.
The Role of Physical Stress
Drawing insights from atomic force microscopy (AFM), the researchers simulated a T6SS attack by applying mechanical force to the bacterial membrane. Their findings indicate that even minor membrane damage can instigate a powerful retaliatory response. This precision in targeting ensures that T6SS acts in response to specific threats, thereby conserving the bacterial resources needed for its operation.
Moreover, the study revealed that the location of membrane ruptures directed the assembly of T6SS components, thereby enhancing the efficiency of their defensive attack. The team posits that a phosphorylation cascade—a series of biochemical reactions—ensures rapid mobilization and accuracy in assembling the T6SS apparatus at the site of membrane disturbance.
Implications for Medicine and Antibiotic Resistance
The implications of this research are particularly significant in the context of antibiotic resistance. Some antibiotics and other chemical agents compromise bacterial membranes, which can inadvertently activate T6SS. This raises concerns about the potential for bacteria like Pseudomonas aeruginosa to develop countermeasures against these medications, particularly in clinical settings where resistance is a growing threat.
Understanding how T6SS functions and how its activation is regulated could provide crucial insights into developing new therapies or inhibitors that thwart this bacterial defense. Researchers are investigating the signaling pathways that activate T6SS and the regulatory mechanisms that turn it off after a threat has been neutralized.
Future Directions
Despite a deeper understanding of T6SS activation, many uncertainties remain. Researchers aim to decipher the complexity behind the activation thresholds of different bacterial strains and how environmental factors, such as mechanical and chemical stress, influence these responses. Additionally, identifying potential protein partners involved in controlling the T6SS could pave the way for innovative strategies to combat antibiotic-resistant infections.
As we advance our knowledge of microbial competition and communication, it becomes increasingly essential to explore the intricacies of these bacterial systems. This ongoing research not only sheds light on survival tactics within the microbial realm but also holds the promise of crafting an arsenal of new therapeutic approaches to tackle some of the most resistant pathogens threatening global health today.
Stay tuned, as the battle between bacteria is not just a microscopic phenomenon; it's a crucial part of the larger narrative in our fight against diseases.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)