
Astronomical Marvel: The Gemini North Telescope Unveils Secrets of a Giant Elliptical Galaxy
2024-10-23
Author: Mei
Astronomical Marvel: The Gemini North Telescope Unveils Secrets of a Giant Elliptical Galaxy
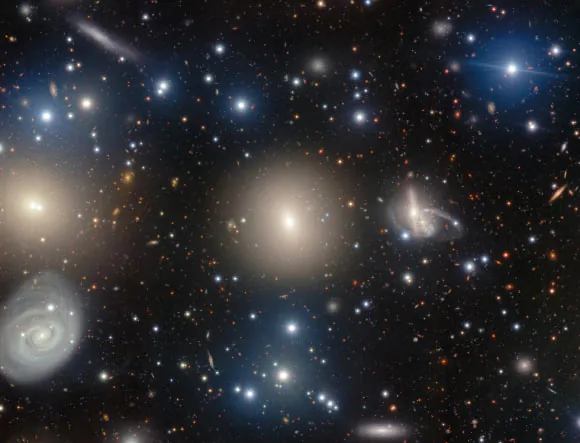
In a stunning showcase of modern astronomy, the Gemini North telescope at NSF's International Gemini Observatory has turned its powerful lens on NGC 1270, a colossal elliptical galaxy residing within the heart of the Perseus galaxy cluster, approximately 250 million light-years away in the Perseus constellation. Utilizing the advanced Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS), astronomers have captured breathtaking images that illuminate the intricacies of this ancient cosmic giant.
Discovered on February 14, 1863, by the German astronomer Heinrich d'Arrest, NGC 1270, also identified as LEDA 12350 or UGC 2660, has an estimated age of about 11 billion years. At a time when the existence of galaxies beyond our Milky Way was still a subject of debate, d'Arrest's discovery contributed to changing perceptions of the universe.
“The initial recognition of NGC 1270 occurred when many celestial objects were still thought to be nebulae, due to their unclear, cloud-like appearances,” noted astronomers from NOIRLab. “It wasn't widely accepted that galaxies, or 'island Universes' as philosopher Immanuel Kant referred to them, existed beyond the limits of our own Milky Way.”
The understanding of the cosmos underwent a significant transformation following the 1920 Great Debate between astronomers Heber Curtis and Harlow Shapley over the nature of such galaxies. This discourse laid the groundwork for later breakthroughs, including Edwin Hubble's 1924 observations that confirmed the existence of galaxies beyond our own. Hubble's work propelled the idea that the universe is teeming with a myriad of galaxies, each as complex and vast as the Milky Way.
Recent observations of NGC 1270 indicate that it is likely home to a supermassive black hole, which is actively consuming matter represented by a brightly lit accretion disk. This phenomenon is only seen in approximately 10% of galaxies, revealing the dynamic and often violent processes taking place in the universe's most massive formations.
The intricate interactions within galaxy clusters like Perseus offer valuable clues about hidden cosmic forces. The existence of such enormous assemblies of galaxies underscores the role of dark matter—the elusive substance thought to exert gravitational influences strong enough to pull galaxies together, forming these dense structures. Current theories suggest that dark matter forms a vast web throughout the cosmos, functioning as the underpinning force that draws galaxies into clusters.
As each image captured by powerful telescopes unveils more details of these 'island Universes,' a tantalizing question remains: What secrets and discoveries will the next phases of exploration reveal? The universe is still shrouded in mystery, and as imaging technology advances, astronomers are poised to uncover profound revelations about our cosmos.
“There’s a sense of excitement as we reflect on a century of discoveries in astrophysics," the astronomers expressed. "With each observation, we inch closer to understanding the true nature of our universe. What revelations await us in the next hundred years?”
Stay tuned for further developments in our quest to unveil the extraordinary wonders that lie beyond our solar system!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)