Astronomers Unveil Incredible Discovery: A New Dense Sub-Saturn Exoplanet Revealed!
2025-01-14
Author: Nur
Introduction
In an exciting breakthrough, an international team of astronomers has announced the discovery of a new exoplanet orbiting a brilliant late F-type star, named TOI-6038 A b. This remarkable alien world is colossal, measuring nearly six times the size and approximately 80 times the mass of Earth. The details of this fascinating finding were released in a new paper published on January 4, 2023, on the arXiv preprint server.
NASA's TESS Mission
NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) has been diligently scanning about 200,000 of the brightest stars in our vicinity, searching for transiting exoplanets. Thus far, it has identified nearly 7,400 candidate exoplanets (TESS Objects of Interest, or TOI), with 591 of those having received confirmation.
Discovery Details
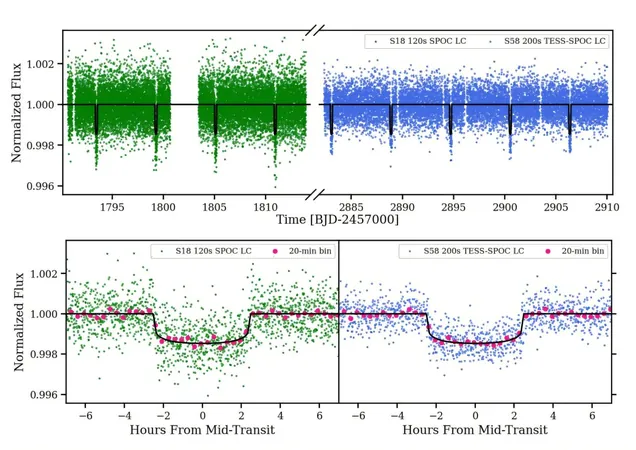
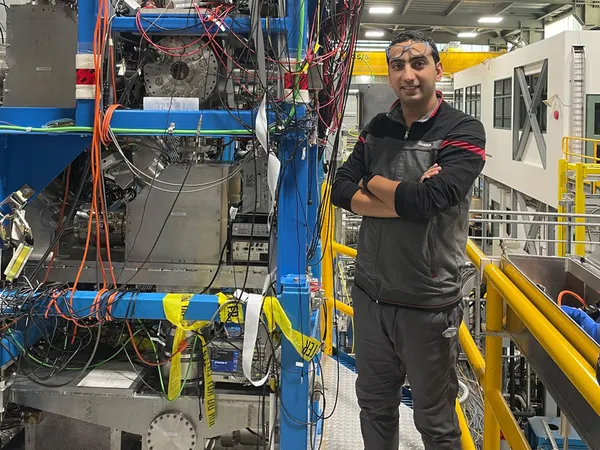
Leading the charge on this latest confirmation is astronomer Sanjay Baliwal from the Physical Research Laboratory (PRL) in Ahmedabad, India. Baliwal's team successfully identified a transit signal within the light curve of TOI-6038 A, which is situated approximately 578 light-years away from Earth. This planetary identity was further confirmed through follow-up observations using the 2.5m telescope at the PRL Observatory.
Characteristics of TOI-6038 A b
The astronomical data reveals that TOI-6038 A b boasts a radius of about 6.41 times that of Earth and a staggering mass of approximately 78.5 Earth masses, leading to a bulk density of roughly 1.62 g/cm³. Orbiting its host star every 5.83 days, TOI-6038 A b is situated a mere 0.069 AU away. Its equilibrium temperature is estimated at a scorching 1,439 K.
Core Composition and Atmosphere
Through intricate modeling of its internal structure, astronomers suggest that TOI-6038 A b has a significant core, weighing around 58 Earth masses and primarily composed of dense materials like rock and iron, accounting for about 74% of its total mass. A modest hydrogen and helium envelope forms the planet's remaining mass, hinting at a comparatively thin atmosphere.
Position in Exoplanet Demographics
This newly discovered exoplanet falls into the category of sub-Saturns, positioned at the threshold between the elusive Neptunian ridge and savanna. What's truly captivating is the demographic of exoplanets in the so-called "Neptunian desert" and "savanna," which illustrates the scarcity of Neptune-like exoplanets in shorter orbital periods and their limited presence at longer distances. They are intriguingly separated by a newly identified overdensity (ridge) of Neptune-like exoplanets with orbital periods between 3-5 days.
Binary Star System
Moreover, TOI-6038 A is part of a binary star system, which includes a K-type star known as TOI-6038 B, located about 3,217 AU away. The main star, TOI-6038 A, has a radius approximately 0.9 times that of our Sun and a mass around 0.86 solar masses. Age estimates suggest this star is about 3.65 billion years old and features an effective temperature of 6,110 K, along with a metallicity of approximately 0.124 dex.
Conclusion
The discovery of TOI-6038 A b adds another layer to our understanding of the diversity and characteristics of exoplanets in our universe. As researchers continue to explore this rapidly evolving field, who knows what other captivating findings await just beyond the stars?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)