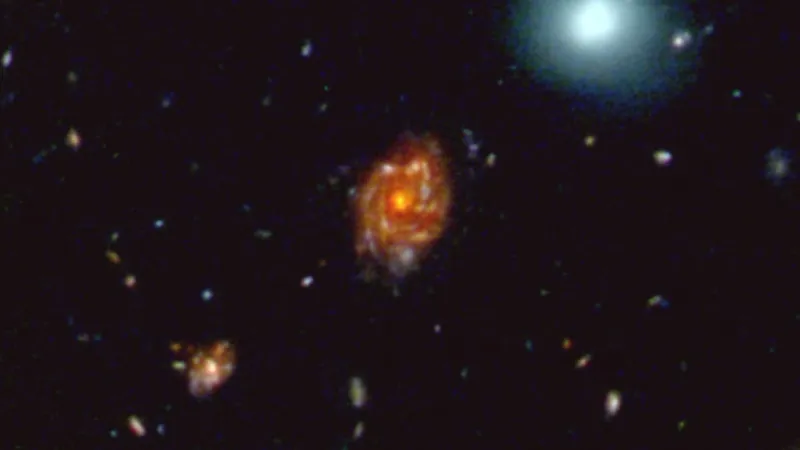

Astronomers Unveil 'Big Wheel': A Giant Spiral Galaxy from the Dawn of Time!
2025-04-04
Author: Siti
Introduction
In an astonishing discovery, a team of astronomers from the University of Milano-Bicocca has identified a colossal spiral galaxy, affectionately dubbed "Big Wheel," that emerged just 2 billion years after the Big Bang—a moment that gave rise to our universe around 13.8 billion years ago. This groundbreaking find highlights the galaxy as one of the largest ever observed from such an early epoch in cosmic history.
Discovery and Characteristics
Utilizing the advanced capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the researchers located Big Wheel in close proximity to a quasar—a brilliantly luminous beacon powered by an actively feeding supermassive black hole. Situated an impressive 11.7 billion light-years away, Big Wheel isn't just massive—it dwarfs our very own Milky Way by five times, sprawling across a remarkable diameter of roughly 100,000 light-years.
Spectroscopic Observations
Through sophisticated spectroscopic observations with the JWST's Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec), the scientists confirmed that Big Wheel operates as a rotating disk, exhibiting a rotation curve characteristic of mature spiral galaxies. This means its rotational speed increases with distance from the center, reaching astounding velocities of hundreds of miles per second—typical of far more evolved galaxies than one would expect at this cosmic stage.
Explaining the Rapid Growth
Adding to the intrigue, Big Wheel's rotational characteristics align with the local Tully-Fisher relationship, a fundamental correlation linking the size and rotation speeds of galaxies observed today. This profound observation suggests that, despite its youth, Big Wheel is exhibiting behaviors comparable to some of the largest and most evolved spiral galaxies found in the current universe. This revelation is particularly striking since it exists at a time when most galaxies are believed to be in their infancy.
Environmental Factors
So, what allowed this massive galaxy to flourish so rapidly? Researchers propose that the environment around Big Wheel may hold the key. Found in a densely populated region of space with galaxy number densities soaring over ten times the cosmic average, Big Wheel likely benefitted from the ideal conditions for accelerated growth. According to co-author Sebastiano Cantalupo, the efficient accumulation of gas might have provided the necessary angular momentum for a spiral galaxy of its size. Additionally, the frequent mergers with gas-rich companions in this crowd could have significantly boosted its size and development speed.
Implications for Cosmology
"This discovery could revolutionize our understanding of early galaxy formation," commented Cantalupo, hinting at the notion that some galaxies might leapfrog the traditionally prolonged process of star formation to achieve enormous mass in the universe's infancy.
Conclusion
The implications of Big Wheel challenge existing cosmological models, as its size and mass starkly surpass what current theories predict for galaxies of its redshift. This extraordinary finding pushes astronomers to reconsider how galaxy formation may transpire under such dense conditions, potentially reshaping our understanding of the cosmos.
As our cosmic narrative unravels, discoveries like Big Wheel forge a new frontier in understanding the evolution and diversity of galaxies, compelling scientists to reconsider the pace and nature of galactic growth in the universe's early chapters. Stay tuned, as the past of the universe increasingly reveals mysteries we thought were once beyond reach!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)