Astronomers Stunned by Discovery of Bizarre 'Ice Balls' in the Milky Way
2025-01-24
Author: Jia
Introduction
In a groundbreaking finding that has captured the attention of researchers, astronomers have discovered two enigmatic icy spheres in a remote corner of the Milky Way galaxy, presenting a cosmic riddle that no one has been able to solve. What exactly are these strange orbs, and what secrets do they hold?
Discovery Details
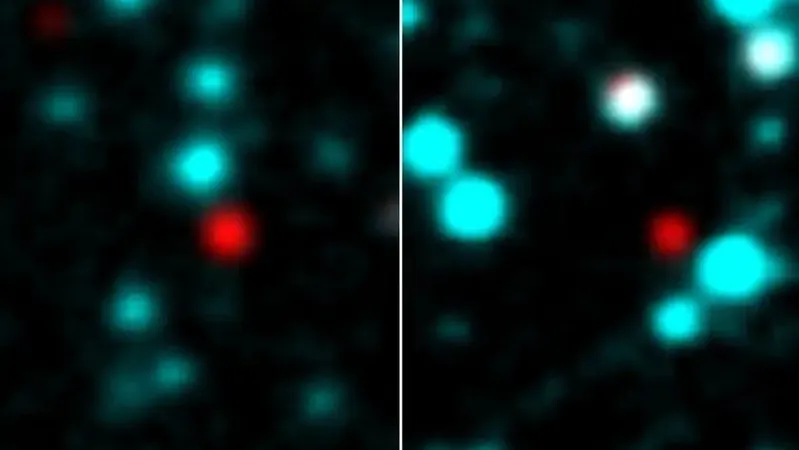
These unusual objects, dubbed “ice balls,” have been identified in the same vicinity of the sky, yet astonishingly, they are separated by an astounding 13,000 light-years and are believed to be completely unrelated. Their existence first came to light in 2021 through data collected by Japan's AKARI space telescope between 2006 and 2011. However, recent observations using the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile have added a new layer of intrigue to this discovery.
Key Questions
The key question remains: Are these icy spheres dense clouds of gas, or could they potentially be an entirely new class of celestial bodies? The strikingly icy appearance of these objects, along with their considerable distance from typical star formation zones, challenges our understanding of cosmic phenomena. Researchers shared their initial findings on January 9 via the preprint server arXiv, although these results are awaiting peer review.
Absorption Features
"Prior infrared observations have revealed that both entities exhibit significant absorption features characteristic of deep ice and dust," the researchers explained. "Such features are typically found in younger stellar formations or background stars obscured by dense matter. However, our ice balls are not located in known star-forming regions or dense clouds. They might indicate a new category of isolated icy objects that we have yet to discover."
Formation Process
To put things into perspective, stars undergo a gradual formation process that can take tens of millions of years, evolving from swirling clouds of dust and gas into luminous protostars before finally emerging as massive spheres of fusion energy akin to our sun. Yet, these peculiar blue balls lie far removed from the dynamics of star creation. Positioned at distances of 30,332 light-years and 43,704 light-years from our sun respectively, they are each over 10 times larger than our solar system.
Comparative Size and Composition
While their size is impressive, it pales in comparison to other gas clouds in the universe, which can expand across vast regions much larger than our entire Milky Way galaxy. Interestingly, the infrared readings surrounding these objects predominantly reveal a mixture of silicon dioxide and carbon monoxide—elements usually associated with young stars. Nonetheless, given their unique icy characteristics and relatively compact size, scientists remain skeptical about whether these objects truly belong to the star family.
Future Implications
This thrilling discovery opens the door to countless questions: What can these ice balls teach us about the formation of celestial bodies? Could they rewrite portions of our cosmic history? As astronomers continue to unravel this cosmic mystery, the scientific community is buzzing with excitement over what might be one of the most significant astronomical revelations in recent years. Stay tuned, because the universe is holding onto some of its deepest secrets, and the journey to uncover them has only just begun!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)