
Astronomers Discover Colossal Water Reservoir in Space – 100 Trillion Times the Volume of Earth's Oceans!
2024-11-04
Author: Rajesh
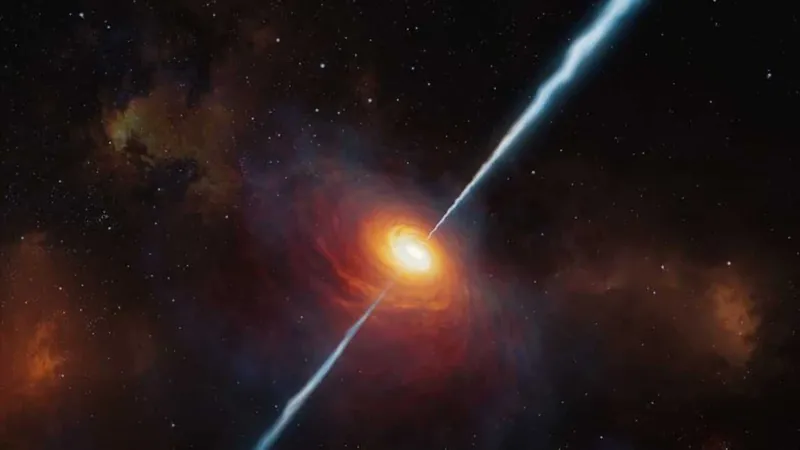
In an astonishing breakthrough, scientists have unearthed a gargantuan water reservoir in the cosmos, bursting with an incredible amount of water estimated to be 100 trillion times the volume of all Earth's oceans combined! This tremendous find potentially reshapes our understanding of water distribution in the universe.
This cosmic reservoir is located around the active quasar known as APM 08279+5255, situated an eye-watering 12 billion light-years away from Earth. At the heart of this luminous quasar lies a supermassive black hole, weighing in at an astounding 20 billion times that of our Sun! The quasar itself emits energy equivalent to that produced by one trillion suns, creating a ferocious gravitational pull that draws in gas, dust, and, as recent findings suggest, a staggering amount of water vapor.
Researchers have discovered that this vast ocean of water stretches across several hundred light-years, painting a picture of a uniquely abundant environment in the universe. The detection of water vapor was facilitated by advanced millimeter and submillimeter technologies, allowing scientists at the Caltech Submillimeter Observatory in Hawaii to observe the quasar using the Z-Spec spectrograph. This powerful tool enabled them to identify the telltale signs of water’s presence at redshift.
In addition, further confirmatory observations were conducted with the Plateau de Bure Interferometer and the Combined Array for Research in Millimeter-wave Astronomy (CARMA). These sophisticated instruments corroborated the initial findings, confirming the existence of this colossal water reservoir that dwarfs anything seen in our own Milky Way galaxy, which contains only a fraction—approximately 4000 times less—of gaseous water and predominantly in frozen forms.
The implications of such a mammoth concentration of water are profound. The extreme environment surrounding the quasar supports the heating of gas to X-ray and infrared levels, demonstrating the dynamic processes at play. Scientists speculate that the supermassive black hole could grow significantly, potentially expanding to six times its current size, fed by the massive amounts of gas surrounding it. Meanwhile, some of this gas may also give rise to new stars, expelling matter from the host galaxy in an intricate cosmic ballet.
This groundbreaking discovery is not just a testament to the wonders of the universe; it also opens new avenues for understanding the early universe's development and the evolution of supermassive black holes. As technological advancements continue to enhance our observational capabilities, who knows what other cosmic secrets await us in the vast expanse of space? Stay tuned as we unlock the mysteries of the universe, one astonishing discovery at a time!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)