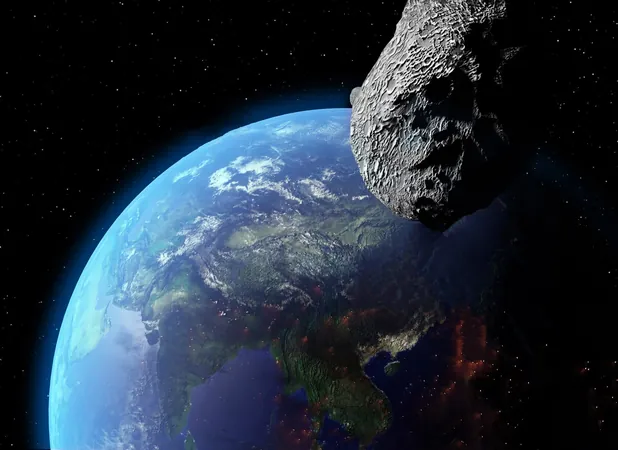

Asteroid 2024 YR4: From Earthly Threat to Potential Lunar Impact!
2025-04-05
Author: Arjun
Introduction
In December 2024, an asteroid known as 2024 YR4 captured the attention of scientists when it was projected to make a close approach to Earth. Initial calculations by experts indicated a 1.3% possibility of an impact on December 22, 2032, which raised alarms across the scientific community, prompting the International Asteroid Warning Network to issue a notification on January 29, 2025.
Tracking Efforts
Zuri Gray, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Helsinki, was part of the team first tracking this celestial body, estimated to be between 40 and 90 meters in diameter. “Our focus has been on monitoring the asteroid’s position, rotation, size, and shape,” Gray commented, highlighting the extensive tracking efforts that commenced in early 2025.
The Nordic Optical Telescope's Role
The Nordic Optical Telescope (NOT) has been pivotal in these observations, as noted by colleague Grigori Fedorets. Located on La Palma, this 2.5-meter telescope has a proven history of detecting near-Earth objects and played a crucial role in refining YR4's trajectory.
Impact Probability Changes
Initially, calculations suggested a rising impact probability of up to 3% for Earth—a record high for a body of this size—but subsequent observations saw the chances plummet to a minuscule 0.001%. However, new data indicated a 4% likelihood of the asteroid impacting the Moon, raising concerns for upcoming lunar missions. Professor Karri Muinonen emphasized, “Should the asteroid hit the Moon, it could unleash particles that might threaten lunar infrastructure and related operations.”
Infrared Observations
In a breakthrough, the James Webb Space Telescope provided infrared observations on March 26, effectively narrowing down the asteroid's diameter to approximately 60 ± 7 meters (197 ± 23 feet). This precision was crucial as thermal emissions offer a more accurate sizing compared to visible light measurements, which can vary due to the object's surface reflectivity.
Significance of Monitoring
The rapid response of the Nordic Optical Telescope has been significant, yielding refined estimates that reduce risks associated with the asteroid. Professor Mikael Granvik noted the importance of agile, high-quality facilities in the ongoing monitoring of potentially hazardous asteroids.
Future Observations and Preparedness
Observations are set to continue until around April or May 2025 when 2024 YR4 will drift beyond the reach of Earth-based telescopes, not to be tracked again until its next close approach in 2028. Plans are underway in Finland to establish a Space Situational Awareness Center, aimed at addressing a range of risks from space threats and enhancing the country's asteroid research capabilities.
Conclusion
While the likelihood of 2024 YR4 impacting Earth has significantly decreased, its 4% chance of striking the Moon highlights a unique potential scenario that could disrupt lunar activities. Asteroids of this scale can inflict considerable damage, emphasizing the importance of ongoing monitoring and preparedness in planetary defense.
Final Thoughts
As scientists gear up for the asteroid's final observable window in spring 2025, the urgency to gather more data intensifies. Future observations could either quell or reignite concerns regarding its trajectory—underscoring the necessity for continued vigilance in an ever-changing cosmic landscape. Stay informed as we follow this thrilling space saga!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)