
Are Mars Missions in Jeopardy? The Hidden Danger of Toxic Dust Could Endanger Astronauts!
2025-03-27
Author: Wei
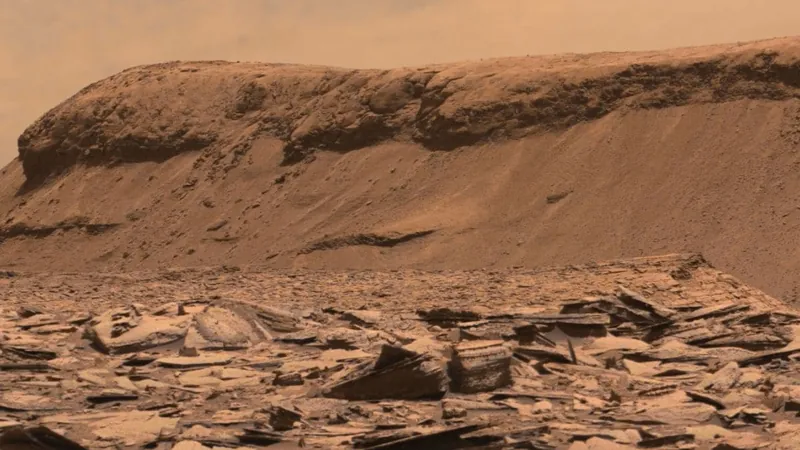
Mars has captured humanity's imagination as a promising destination for exploration, with NASA and the China National Space Administration (CNSA) planning ambitious crewed missions to the Red Planet in the near future. However, alarming new research indicates that the toxic dust prevalent on Mars may pose a serious threat to the health and safety of astronauts during these missions.
A recent study in the journal GeoHealth reveals that the fine, electrostatically charged dust on Mars is laden with hazardous materials, including silica, perchlorates, gypsum, and nanophase iron oxides. When inhaled, these substances can result in severe respiratory conditions, thyroid dysfunction, and potentially life-threatening diseases.
Experts from institutions including the Keck School of Medicine at USC, the UCLA Space Medicine Center, and NASA's Johnson Space Center collaborated on this crucial research, underscoring the urgent need for effective strategies to mitigate these dangers for future astronauts.
The Peril of Martian Dust Storms
On Mars, every Martian year—lasting roughly 687 Earth days—regional dust storms arise, particularly during the southern hemisphere's summer. Every third Martian year, these storms escalate into global events that cloak the entire planet, becoming visible from Earth.
These dust storms have already proven disastrous for robotic missions; for instance, NASA's Opportunity Rover was rendered inoperable in 2018 due to dust accumulation on its solar panels. Similarly, the InSight Lander lost functionality in 2022, illustrating the serious hazards posed by Martian dust.
For human missions, the potential health consequences are even graver. Martian dust's unique jagged structure makes it particularly harmful, as it can damage lung tissues and other delicate biological structures more effectively than rounder Earth dust, which has weathered over time.
Profound Health Risks from Martian Dust
One major concern is how deeply Martian dust can infiltrate the respiratory system. "Astronauts could face exposure to multiple toxic elements on Mars," warns Dr. Justin Wang, a medical researcher at USC. Silica, prevalent in Martian dust, poses significant risks, potentially leading to silicosis—a lung disease frequently seen in miners on Earth.
Moreover, the presence of perchlorates in Martian dust may disrupt thyroid function, leading to serious blood disorders like aplastic anemia, characterized by insufficient blood cell production. Given the already heightened risk of pulmonary diseases due to radiation exposure in spaceflight, the introduction of silica and iron oxides could exacerbate astronaut health concerns even further.
Just as Apollo astronauts experienced respiratory issues from lunar dust, which was fine and airborne, Martian dust may inflict similar yet more dangerous effects due to its heavy metal content—such as chromium, beryllium, arsenic, and cadmium—that link to severe health issues.
Engineering Challenges of Martian Dust
Beyond health risks, Martian dust poses significant technical challenges for spacecraft, habitats, and equipment. Dust continually falls on surfaces, and during global storms, it can accumulate to considerable depths. This dust can hinder solar panels, landers, and spacesuits, threatening mission success if not properly managed.
Professor Brian Hynek from the University of Colorado Boulder emphasizes the importance of addressing dust issues, noting that failure to implement effective maintenance strategies could lead to mission failures similar to those encountered by past rovers.
Strategies for Mitigation
Considering that the round-trip mission to Mars may last up to three years, with astronauts spending a significant amount of time on the Martian surface, effective medical interventions become essential. Unlike missions to the ISS or the Moon, rapid evacuation from Mars is not an option due to distance.
Preventive measures, including advanced air filtration systems, cabin cleaning techniques, and electrostatic devices to minimize dust accumulation, are in development. Additionally, dietary interventions—like vitamin C to mitigate chromium exposure—are being explored. However, experts caution that over-supplementation could come with its own health risks.
NASA and other space agencies are actively investigating innovative technologies to tackle the dangers of Martian regolith, including protective coatings, specialized sprays, and electron beams to minimize dust adherence.
The Road Ahead
Natalya Zavina-James from the UK Space Agency highlights the critical importance of addressing the health implications of Mars exploration, noting that ethical considerations regarding astronaut safety must be prioritized.
Despite the risks associated with Martian dust, experts believe that these challenges can be overcome with careful preparation. "While the dust on Mars poses risks, they are manageable with the right strategies in place," Dr. Wang states.
As the Artemis program progresses and plans for Mars take shape, a comprehensive understanding of the medical, engineering, and operational challenges will be vital in ensuring astronauts' health, safety, and success on this remarkable journey to the Red Planet. Stay tuned for further updates as we prepare to venture into the unknown!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)