
Antarctica's Hidden Guardian: Is It Under Threat from Climate Change?
2025-05-23
Author: Nur
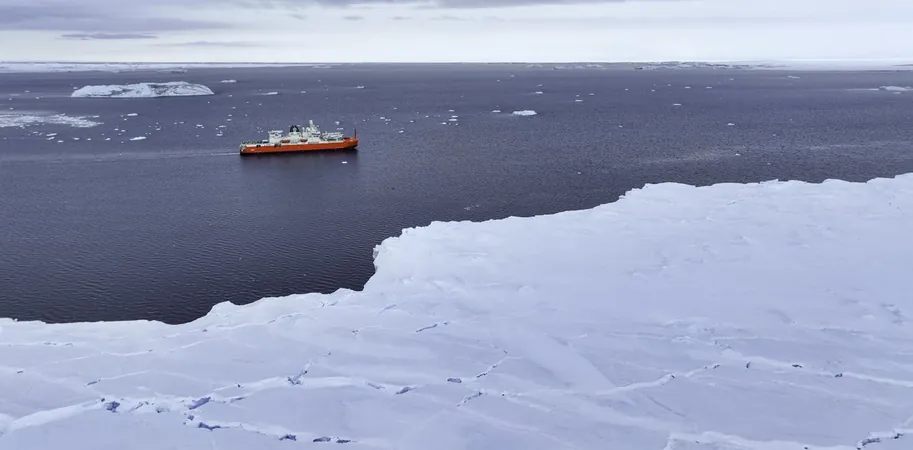
Deep in the icy realms of Antarctica lies a little-known ocean current, a powerful shield against the warm waters creeping in from the north. However, recent research reveals that this crucial barrier is under serious threat as melting ice disrupts its stability.
Scientists have discovered that meltwater from Antarctica is not only accelerating the Antarctic Slope Current but is projected to boost its speed significantly by mid-century. While a quicker current may seem beneficial, it could lead to greater instability, allowing warm water eddies to gnaw away at Antarctica's ice, which could have dire consequences for our planet's climate system.
The implications of increased ice melt are staggering. As Antarctica thaws, global sea levels rise. Even modest increases can double the likelihood of devastating floods in coastal areas around the world. Alarmingly, prior studies indicate that the influx of meltwater is also disrupting the intricate network of deep ocean currents, which play an essential role in transporting heat, nutrients, and water across the globe.
This makes it vital to minimize ice loss in Antarctica, crucial for stabilizing our global climate. The Antarctic Slope Current, which transports ocean water westward along the continental slope, is integral to protecting the ice from warmer waters. While it can't completely prevent melting, it does slow down the process, helping maintain Antarctica’s icy fortress.
Using high-resolution ocean-sea ice models, researchers examined how the Antarctic Slope Current responds to shifts in wind patterns, heat levels, and increased meltwater. They found a 14% uptick in current speed over the past quarter-century, with a staggering 49% rise expected in the next 25 years.
But there’s more at stake than just faster currents. The additional meltwater makes surrounding ocean waters less salty and therefore lighter, altering the very structure of the Antarctic Slope Current. This causes dense coastal waters—key players in the global overturning current network—to slow down, allowing warmer waters to edge closer to Antarctica.
Initially, one might think that a stronger Antarctic Slope Current could better shield the continent from warming waters to the north. But climate change brings complexity; faster currents generate turbulence, creating eddies that transport warm water toward the ice. It's a counterintuitive twist—while the current may become reinforced, the eddies pose a formidable threat, amplifying the melting effect.
The fate of Antarctica is riddled with uncertainty, yet one thing is abundantly clear: this frozen frontier is vital to the stability of global climate systems. The Antarctic Slope Current, once a diligent protector, is now being altered by the very ice it safeguards.
The time for action is now. Humanity must work urgently to cut carbon emissions to protect this natural fortress. When it comes to preserving the Antarctic Slope Current, there’s no option to wait—it's our only hope for maintaining balance in our climate system.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)