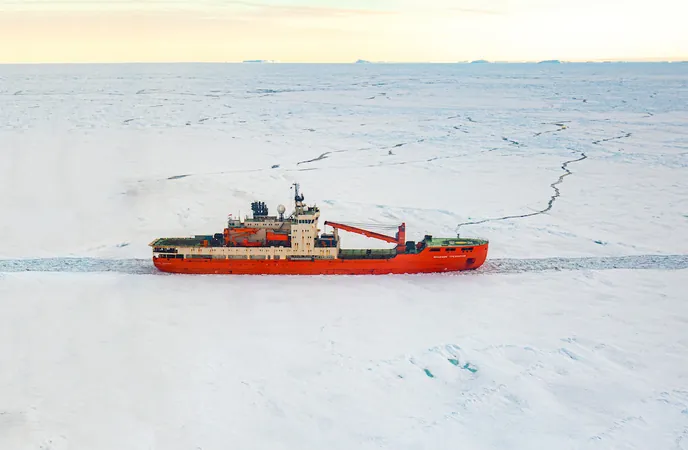

Antarctica in Crisis: Microplastics and Melting Ice Signal Global Alarm
2025-06-16
Author: Siti
A Polar Expedition Uncovers Alarming Changes
During a groundbreaking 70-day mission aboard the Russian icebreaker Akademik Tryoshnikov, a dedicated team of 57 researchers has documented alarming changes in Antarctica. Their findings reveal rapidly melting glaciers, expanses of moss spreading across the ice, and an unsettling presence of microplastics dotting the continent.
The Heart of Climate Regulation
Antarctica, the world’s fifth-largest continent, plays a crucial role in regulating Earth’s climate. Alongside the Arctic, it acts as a thermal balancer by redistributing heat from the equator, helping to stabilize global temperatures. Led by Brazilian glaciologist Jefferson Cardia Simões, this expedition was vital in understanding how climate change is impacting this frozen frontier.
Unveiling Hidden Secrets
The researchers navigated approximately 29,000 kilometers (about 18,000 miles), drilling deep into ice layers to gather snow and seawater samples. These layers record historical atmospheric conditions, sparking concern over the documented microplastic contamination.
Filipe Lindau, head of the glaciology team, explains that these precious samples reveal essential information about past climates and current environmental degradation.
Microplastics: A New Presence
Onboard climatologist Venisse Schossler confirmed that microplastics were found in seawater samples, visible through specialized strainers. This alarming discovery highlights how pervasive plastic pollution has even reached the remotest parts of our planet.
Glacier Retreat: A Startling Reality
The team also meticulously measured the retreat of glaciers during their expedition. Climatologist Francisco Aquino reported that the Lange Glacier has receded by at least 400 meters in just three decades, with significant losses recorded over the past few decades.
A Dangerous Chain Reaction
Research from the U.S. National Snow and Ice Data Center indicates that rising temperatures have reduced Antarctic sea ice by an alarming 6,500 square kilometers (2,500 square miles) since 2016, disrupting the intricate food chain reliant on krill, the foundation species of the Antarctic ecosystem.
Atmospheric Links to the Amazon Rainforest
Diving deeper into environmental interconnections, researchers revealed that atmospheric currents connect Antarctica to the Amazon rainforest, demonstrating how deforestation in the Amazon can send smoke and pollution impacts as far south as Antarctica. The heavy particulates contribute to the melting glaciers by reducing their ability to reflect sunlight.
Impact on Wildlife
This climate shift poses dire consequences for iconic wildlife such as penguins, which are adapted to snowy conditions rather than rain. Polar biologist Emanuele Kuhn warns that increased rainfall can lead to hypothermia in penguin chicks, impacting their survival rates.
A Call for Global Awareness
Researchers stress the urgency for greater focus on Antarctica in climate discussions, asserting that the health of polar ecosystems is interconnected with tropical regions. Simões states that polar oceans serve as carbon sinks, absorbing massive amounts of CO2, and their degradation could lead to catastrophic increases in atmospheric carbon levels.
Antarctica: The Silent Alarm
As Lindau aptly puts it, ‘Despite its isolation, Antarctica influences global climate regulation harmoniously, making it crucial for everyone to recognize its importance.’ The expedition underlines that by ignoring the deepening crisis in Antarctica, we risk overlooking a vital part of the Earth’s climate system that affects us all.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)