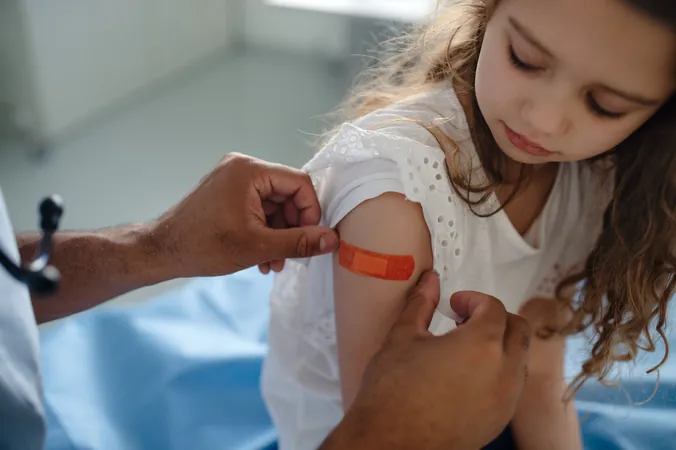
Anonymous Data Distorts Dutch Vaccine Stats Amid Cultural Challenges
2025-07-08
Author: Siti
Anonymous Reporting Affects Vaccination Statistics
In recent developments, the Dutch Public Health Institute (RIVM) revealed to Euractiv that the rise in anonymous data reporting is impacting public vaccination registration. Their 2025 report highlights a troubling decline in vaccination rates, particularly among infants and toddlers, while noting an increase in HPV vaccinations.
Declining Accuracy in Vaccination Reporting
Since 2022, individuals have had the option to decline sharing personal details, such as birth dates, which means registered vaccination coverage appears lower than reality. A spokesperson from RIVM mentioned that this opt-in policy will be reevaluated with potential changes expected by late 2025.
Critical Demographics Facing Decreased Coverage
The RIVM's analysis indicates that vaccination rates have significantly dropped among Dutch children of Moroccan or Turkish descent, as well as those from large families not enrolled in formal childcare. To combat these trends, RIVM is enhancing communication strategies and collaborating with healthcare professionals to better reach underserved communities.
Concerns Over Disease Outbreaks
With declining vaccination coverage, RIVM warns of potential outbreaks of infectious diseases. The type of primary school also plays a role; vaccination rates have sharply decreased in Islamic schools, and remain low in orthodox Protestant and anthroposophical institutions. This scenario heightens the risk of diseases like measles spreading within these clusters.
Positive Trends in HPV Vaccination
On a slightly brighter note, HPV vaccine coverage has risen, especially among boys, with campaigns targeting those aged 26 and under likely contributing to this increase. However, the RIVM reported an uptick in whooping cough cases along with measles and mumps, primarily linked to infections carried back from travels abroad.
Challenges in Meeting Vaccination Goals
Despite efforts, the RIVM can no longer confirm that the Netherlands is achieving the WHO's target immunization rates, particularly for the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. Initiatives are underway to address vaccine hesitancy, including informative online platforms and dedicated hotlines like the 'Twijfeltelefoon' (doubt hotline), aiming to assist those with concerns about vaccinations.
As the landscape of vaccine acceptance continues to shift, the need for effective communication and outreach strategies has never been more critical.
 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)