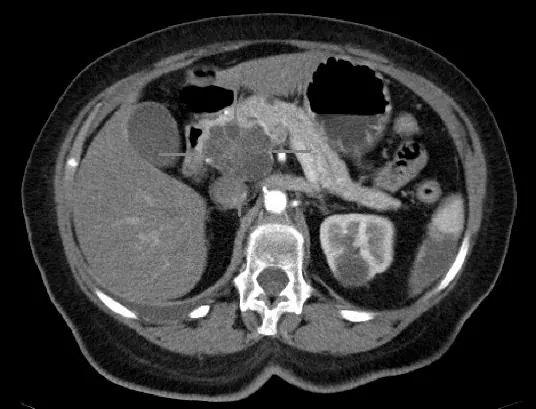
Alarming Survey Reveals Ignorance About Rising Pancreatic Cancer Risk in Younger Adults
2024-10-30
Author: Mei
In a striking revelation, a recent survey from The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center has highlighted a concerning lack of knowledge among adults under 50 regarding pancreatic cancer—a disease that is increasingly affecting younger populations. While traditional perceptions depict pancreatic cancer as primarily an affliction of the elderly, the truth reveals a rising incidence rate among adults in their 40s, with some experts urging immediate action to address this knowledge gap.
The survey found that more than half (53%) of respondents under 50 are unaware of the early warning signs of pancreatic cancer. Additionally, a staggering 37% expressed resignation, believing there’s nothing they can do to alter their risk, while 33% thought that only older adults face dangers associated with this aggressive cancer.
Dr. Zobeida Cruz-Monserrate, a leading figure at OSUCCC—James, emphasized the troubling trend of rising pancreatic cancer rates, which have increased by about 1% per year. The growing occurrence of the disease within younger demographics calls for critical research efforts to investigate the underlying reasons.
So, what can be done? Dr. Cruz-Monserrate accentuates the importance of maintaining a healthy weight as a significant lifestyle change that could help mitigate the risk. Alarmingly, one-third of Americans are classified as overweight, with over 40% designated as clinically obese—this alone elevates the risk of pancreatic cancer by 20%. While hereditary factors account for a mere 10% of pancreatic cancer cases—linked to genetic markers like BRCA genes and Lynch syndrome—Dr. Cruz-Monserrate points out that lifestyle choices are largely in an individual’s control.
In stark statistics, projections indicate that over 66,000 Americans will receive a pancreatic cancer diagnosis in 2024, with survival rates grim; less than 13% are expected to live beyond five years after diagnosis.
Further contributing factors that individuals can modify include the elimination of alcohol consumption, engaging in regular exercise, and opting for a plant-based diet with minimal red and processed meats. Encouragingly, the survey noted that 54% of respondents recognized the importance of genetic testing, which can guide individuals on whether screening for pancreatic cancer is advisable.
Ongoing research at OSUCCC—James aims to develop innovative screening methods for early detection of pancreatic cancer, including non-invasive techniques for analyzing pancreatic cysts and exploring the links between diabetes, chronic pancreatitis, and cancer risk.
Dr. Cruz-Monserrate cautions that pancreatic cancer often remains “a silent killer,” showing no symptoms until it reaches advanced stages. She urges that changes in lifestyle, alongside a clear understanding of one’s family medical history, are essential in combating this deadly disease. "We must continue to aggressively pursue research that will enhance our capabilities to prevent, diagnose, and treat this cancer more effectively," she stated, emphasizing the pressing need for awareness and action.
The survey results serve as a stark reminder: knowledge is power. Awareness about pancreatic cancer and proactive measures could save lives in this growing demographic. Are you informed enough to take action?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)