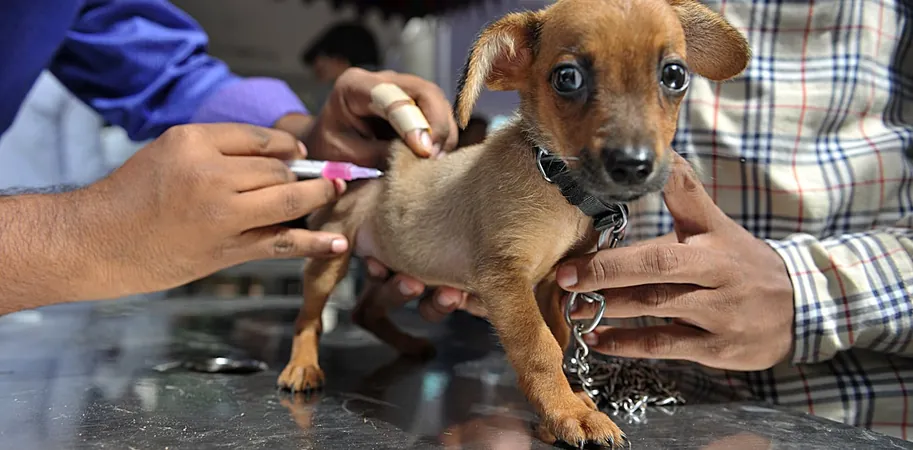

Alarming Rise in Vaccine Hesitancy Among Pet Owners – What It Means for Public Health
2025-01-14
Author: Siti
Alarming Rise in Vaccine Hesitancy Among Pet Owners – What It Means for Public Health
In an era where preventive health measures are paramount, the growing vaccine hesitancy among pet owners is raising alarm bells for experts and public health advocates alike. While humans have been the focus of vaccine discussions—especially in light of the COVID-19 pandemic—our beloved furry companions also require protective vaccinations to fend off severe diseases that can lead to outbreaks.
Recent research, set to be published in the American Journal of Veterinary Research and the Journal of Vaccine in 2024, highlights a disturbing trend of vaccine hesitancy spilling over into the pet-owning community. This pattern threatens not only pet health but also poses broader implications for societal wellbeing.
Why Vaccines are Essential for Pets
Vaccinations play a critical role in safeguarding both individual animals and public health. Vaccines offer direct protection by significantly reducing the risk and severity of contagious diseases. Furthermore, by achieving herd immunity—where a large portion of a population is vaccinated—the spread of disease is curtailed, benefiting not just the vaccinated individuals but the entire community.
While pets like dogs and cats greatly benefit from vaccines, research on pet vaccination rates is sparse. However, the findings of the recent study provide both good news and cause for concern. The vast majority of pets receive core vaccines, including those protecting against rabies, which is paramount for both animal health and human safety. An impressive 75% of pet owners reported trusting their veterinarians regarding vaccination advice.
A Growing Concern: Vaccine Hesitancy in Pets
Despite these positives, the study unveiled troubling statistics: about 22% of dog owners and 26% of cat owners expressed hesitancy regarding vaccinating their pets. Shockingly, around 4% of dogs and 12% of cats are unvaccinated against rabies, while rates for diseases such as parvovirus and distemper are even more concerning.
Many pet owners mirror the vaccine hesitancy seen in humans, with over half questioning the effectiveness of vaccinations and expressing worries about potential side effects. A significant number believed their pets could develop immunity naturally through exposure to diseases. This mindset poses significant risks to both pets and humans, given that unvaccinated pets can become vectors for catching and spreading diseases like rabies.
Broad Implications for Public Health
The ramifications of unvaccinated pets extend beyond individual cases. Pet owners may face increased financial and emotional burdens due to preventable illnesses in their pets. Veterinarians and pet-related professionals could encounter a resurgence of diseases that have become uncommon, leading to possible outbreaks and increased healthcare costs.
From a public health perspective, a significant decline in pet vaccination not only threatens animal welfare but also raises the risk of zoonotic diseases that can be transmitted to humans. Infection from rabid animals can have dire consequences, especially for those exposed during outdoor activities.
Moving Forward: Strategies to Combat Vaccine Hesitancy
Addressing this crisis requires a comprehensive public health strategy tailored to the needs of pet owners. Instead of dismissing their concerns, stakeholders—including veterinarians, public health officials, and animal welfare organizations—should engage pet owners in constructive conversations. By providing accurate information and addressing misconceptions about vaccines, we can work to rebuild trust and encourage higher vaccination rates for pets.
As the saying goes, 'A vaccinated pet is a happy pet.' Now is the time to ensure that our four-legged friends receive the protection they deserve, ultimately benefiting both pets and their human counterparts in the fight against infectious diseases.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)