AI Takes Aim at Heart Disease: Uncovering Risks for Older Hypertensive Patients
2025-01-11
Author: Nur
AI Takes Aim at Heart Disease: Uncovering Risks for Older Hypertensive Patients
In an alarming revelation, the global crisis of hypertension – a condition affecting 1.3 billion adults as of 2019 – continues to wreak havoc, particularly among older adults. With a staggering 330 million individuals in China alone suffering from cardiovascular diseases, 245 million cases can be directly linked to hypertension. This dire situation is compounded by the reality that hypertension contributes to nearly 10.8 million deaths each year, echoing the urgent need for effective monitoring and intervention strategies.
The burden is especially heavy for older hypertensive patients, who face poorer prognoses in terms of heart disease outcomes. The escalating rates of hypertension among the aging population call for early identification of high-risk individuals. This need fuels the ambition of researchers to harness machine learning technologies for predicting heart disease risk. The development of predictive models could pave the way for personalized interventions, significantly enhancing the quality of life for this vulnerable group.
In recent years, traditional regression methods have struggled to navigate the complexities of nonlinear relationships in large datasets. Enter machine learning, a potent tool gaining traction within the medical field. Models such as Logistic Regression (LR), XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting), and Deep Neural Networks (DNN) are emerging as formidable allies in the fight against heart disease, allowing for more accurate predictions and interventions based on individuals’ medical histories, demographics, and lifestyle choices.
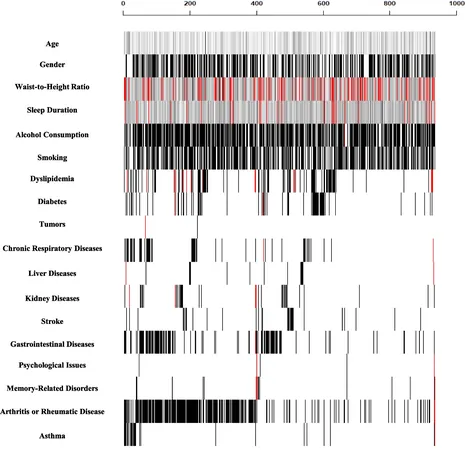
This groundbreaking study utilized data from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS), a comprehensive longitudinal dataset that followed participants aged 45 and above. Data from 934 older hypertensive patients were meticulously analyzed, with an astonishing 26.03% developing heart disease within seven years. Researchers identified critical risk factors such as age, dyslipidemia (abnormal cholesterol levels), chronic lung diseases, and lifestyle habits, including smoking and alcohol consumption, which were shown to heighten the risk of heart disease.
Through rigorous data processing, including outlier detection and feature engineering, the researchers constructed predictive models and compared their effectiveness. The XGBoost and DNN models demonstrated significant advancements in sensitivity and overall predictive capability, especially after refining the feature set to focus on the most impactful variables. Notably, DNN achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.67, indicating a robust predictive power when assessing heart disease risk among older patients.
The analysis also illuminated the nontrivial relationship between various lifestyle factors and heart disease risk. For example, increased alcohol consumption was linked to a higher probability of heart disease in older patients, while demographic variables such as waist-to-height ratio emerged as significant predictors. These insights stress the importance of integrating lifestyle interventions in managing hypertension and preventing heart disease with targeted public health initiatives.
Despite the advancements presented in this study, researchers acknowledged limitations, including the potential lack of generalizability due to the sample size and the absence of external validations. However, the implications of these findings are profound, underscoring the urgent necessity for healthcare professionals to implement machine learning models for early risk identification and intervention strategies.
In summary, as the global population ages, the integration of machine learning within healthcare holds transformative potential for managing hypertension-related heart disease. This study serves as a clarion call for the development of personalized healthcare solutions that prioritize early intervention, ultimately saving lives and improving the quality of care for older hypertensive patients. Stay tuned as we unveil more insights into the future of healthcare powered by artificial intelligence in disease prediction!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)