A Shocking Discovery: Supermassive Black Hole in Andromeda Exhibits Dazzling Variability!
2025-04-03
Author: Siti
In a groundbreaking revelation, a researcher from Michigan State University has identified mysterious fluctuations in X-ray emissions from a supermassive black hole located in the Andromeda galaxy. Using the renowned NASA Chandra X-Ray Observatory, Stephen DiKerby, a physics and astronomy research associate, was astounded to witness the black hole's flickering light.
"Every large galaxy harbors a supermassive black hole, yet the intricate dynamics of their relationship remain largely enigmatic," DiKerby stated. "When I analyzed the data captured by the Chandra telescope, a chill ran down my spine—I was observing the X-rays from a supermassive black hole blinking on and off!"
Supermassive black holes, which can be millions to billions of times more massive than our sun, are among the universe’s most compelling mysteries. With their gravitational pull so powerful that not even light can escape, these cosmic giants can heat surrounding material to extreme temperatures, creating intense X-ray emissions detectable by orbiting telescopes like Chandra.
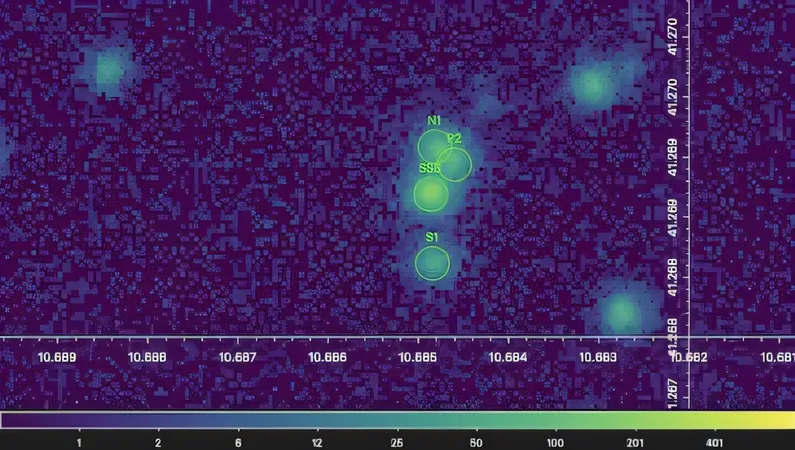
DiKerby, an active member of the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, and his team meticulously examined fifteen years of data from Chandra, constructing a comprehensive record of X-ray emissions from the Andromeda galaxy’s supermassive black hole, known as M31*.
This research sheds light on the complex interplay between galaxies and their black holes, which is pivotal for understanding cosmic evolution over the last 14 billion years. The findings were recently published in *The Astrophysical Journal*, marking a significant contribution to the field.
The Journey Begins with Neutrinos
Interestingly, the narrative doesn’t commence with black holes but rather with neutrinos—subatomic particles that powerfully influence cosmic phenomena and may originate from environments surrounding supermassive black holes like M31*. DiKerby and his team followed these elusive particles as they traverse space, acting as trail markers that could unlock the secrets of extreme astronomical systems.
DiKerby commented on the capabilities of the Chandra telescope, stating, "Its remarkable spatial resolution allows us to isolate X-ray emissions from M31*, despite the presence of three other X-ray sources in close proximity. It’s the only telescope equipped to accomplish this task." The team likened their data analysis to zooming in on various flickering candles scattered across the expanse of a football stadium.
Their compelling findings reveal that M31* has been in an active state since 2006, marked by significant X-ray flares, with another flare detected in 2013. This ties in with recent IceCube observations that linked similar flares in another galaxy to their respective supermassive black holes, suggesting these eruptions could indicate potential neutrino emissions—an exciting connection between different cosmic events.
The Future of Observational Astronomy at Stake
Despite the triumphs of the Chandra telescope, its future hangs in the balance due to looming funding concerns. As scientists focus on developing the new generation telescope, AXIS, which is not expected to become operational until the 2030s, the urgency of preserving the capabilities of Chandra grows.
"If Chandra loses its funding, the opportunity for high-resolution observations will vanish," DiKerby warned. He expressed hope that their paper inspires ongoing research into M31*, emphasizing the necessity of continuing to observe and analyze these cosmic wonders while working on the next generation of telescopes.
"I urge everyone to keep their eyes on this exciting system, documenting the flares and unraveling the narrative of supermassive black holes," DiKerby concluded. With each new discovery, we inch closer to understanding the universe’s most formidable enigmas. Is this the beginning of an entirely new chapter in astronomical research? Only time will tell!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)