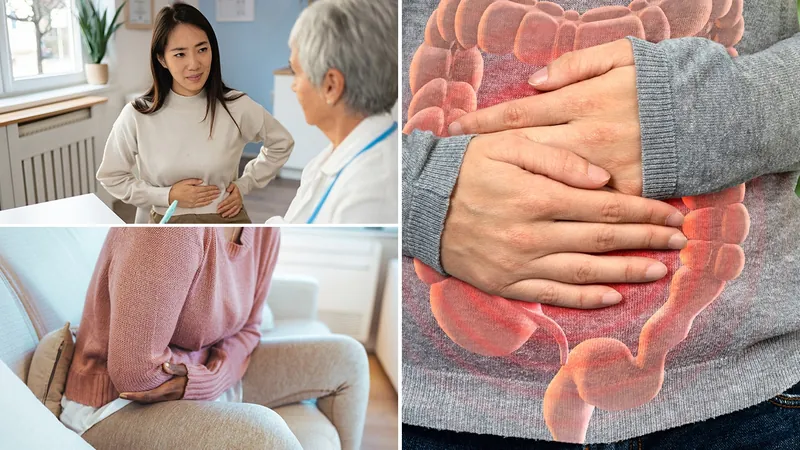
3 Essential Diet and Health Tips for Managing IBS Symptoms Effectively
2024-09-20
Understanding IBS: Diagnosis and Symptoms
IBS is characterized by a range of symptoms, which may include abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Medical professionals rely on a patient's reported symptoms to diagnose IBS, applying criteria established by the Rome Foundation, a recognized leader in gut-brain interaction disorders. Symptoms often manifest in cycles of constipation and diarrhea, necessitating a tailored approach to management. If you are experiencing persistent digestive issues that disrupt your daily activities, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider who can help diagnose the problem, possibly identifying IBS as the underlying cause.
1. Dietary Adjustments: The Low FODMAP Diet
One of the most effective dietary strategies for IBS management is the Low FODMAP Diet. FODMAPs—short for fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols—are types of carbohydrates that can be challenging for some individuals to digest. Studies have shown that following a Low FODMAP Diet can lead to significant symptom relief. Patients are encouraged to eliminate high FODMAP foods such as certain fruits (like apples and pears), vegetables (like onions and garlic), wheat products, and artificial sweeteners, focusing instead on low FODMAP alternatives. These might include bananas, carrots, and gluten-free grains.
2. Lifestyle Changes: Stress Management and Mental Health
Beyond dietary changes, incorporating stress-reduction techniques is vital for managing IBS. Stress is a significant trigger for many patients, and practices such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture can offer significant relief. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is also beneficial, allowing individuals to better cope with the psychological aspects of IBS. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can improve bowel function and reduce the severity of symptoms. It's important to tailor exercise routines to individual tolerance levels and find enjoyable activities.
3. Medication and Ongoing Management
For some individuals, dietary adjustments and lifestyle changes may not be enough. Medications can be prescribed based on predominant symptoms, such as antidiarrheal medications for diarrhea or laxatives for constipation. New treatments are continuously being researched, and staying informed about advancements in IBS management is key.
Conclusion: A Lifelong Journey
For the majority of IBS sufferers, the condition is a lifelong challenge. Symptoms can vary greatly among individuals; some may have severe sensitivities to certain foods, while others may find some relief from ostensibly problematic foods. As a general rule, it is advisable for those with IBS to avoid high-fat foods, fried items, and artificial sweeteners, which can worsen digestive discomfort. Despite the challenges presented by IBS, with informed dietary decisions and a supportive lifestyle, individuals can achieve a much higher quality of life. Consulting with healthcare professionals and creating personalized management plans are crucial steps for effective IBS control. Always remember: You're not alone in this!




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)