Whooping Cough Cases in the US Reach Alarming 10-Year High—What You Need to Know!
2024-12-25
Author: Ying
Overview of Whooping Cough Surge in the US
The United States is facing a concerning surge in whooping cough cases, with more than 32,000 infections reported so far in 2023. This marks a dramatic increase, escalating to approximately six times the number of cases that were reported at the same time last year. The last time the nation saw numbers this high was in 2014, according to preliminary data released by the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
What is Whooping Cough?
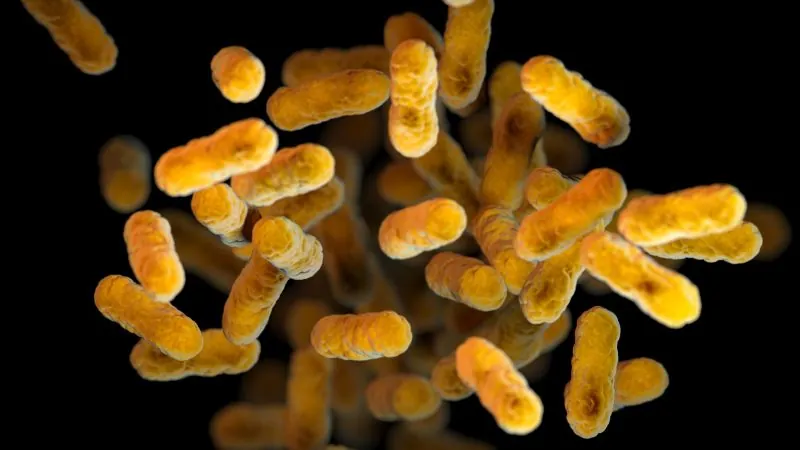
Whooping cough, also known as pertussis, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the bacterium Bordetella pertussis. The infection often begins with mild symptoms resembling the common cold, such as a runny nose, sneezing, and a low-grade fever. However, as the days progress, patients can develop a debilitating, painful cough that may last for weeks or even months. These coughing fits can be intense enough to cause vomiting or rib fractures, typically accompanied by the characteristic 'whooping' sound as individuals struggle to breathe.
Factors Contributing to the Increase in Cases
This recent spike in cases reflects a troubling trend as infections that had previously declined during the COVID-19 pandemic are now on the rise again. Health experts believe that the return to pre-pandemic social interactions and an overall decline in vaccination rates may be contributing to this resurgence.
Geographical Impact
The Midwest has been particularly hard hit, accounting for about a quarter of all cases reported. States like Pennsylvania are leading in total cases, raising alarms about the vulnerabilities within various communities.
Who is at Risk?
Children under one year old are especially at risk for severe complications from whooping cough, as their immune systems are still maturing. This risk is exacerbated among infants who have not yet received all their recommended vaccinations. The CDC strongly advocates for vaccination as a preventive measure—children should receive the DTaP vaccine, while adolescents and adults should get the TDaP booster for ongoing protection.
Vaccination Rates and Importance
Sadly, vaccination rates have dipped, particularly among kindergartners, where approximately 92% have received the DTaP vaccine for the 2023-2024 school year. This figure is below the federal target of 95%, indicating that thousands of young children may be left vulnerable to this preventable disease. Additionally, the immunity provided by the vaccine can wane over time, making it crucial for individuals to keep their vaccinations current.
Treatment Options
While antibiotics can effectively treat whooping cough if administered in the initial weeks of infection, the treatment options become limited once the cough intensifies. At this stage, patients are primarily advised to manage their symptoms by resting and staying hydrated, as the infection runs its natural course.
Conclusion and Call to Action
As we move into the winter months, the landscape of respiratory illnesses is changing; although overall activity remains moderate, both COVID-19 and flu cases are showing signs of resurgence. The unfolding situation calls for heightened vigilance, as parents and guardians are urged to ensure their children are fully vaccinated as a safeguard against this contagious disease. Stay informed and protect your loved ones—this is the moment to take action against whooping cough! *Is your child vaccinated? Check their immunization status today and help us keep the community safe!*


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)