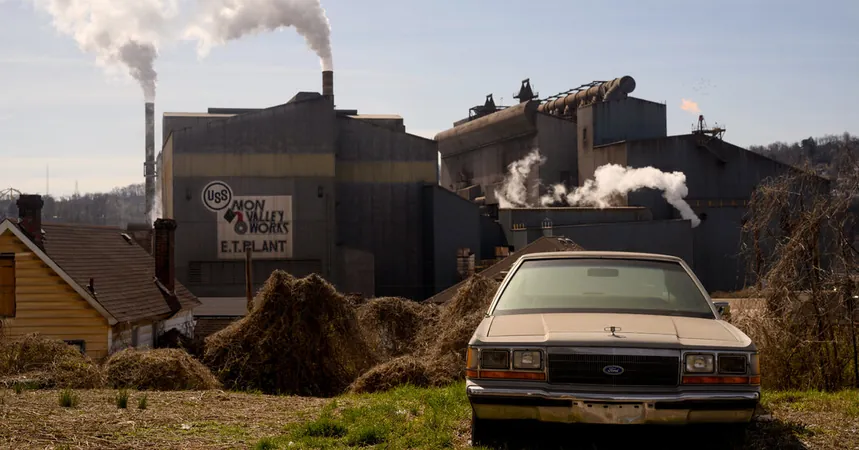

U.S. Steel’s Dire Future: What Happens After the Nippon Steel Merger Fails?
2025-01-09
Author: Jessica Wong
Introduction
For over a year, U.S. Steel, once a hallmark of American industrial power, set its sights on a precarious merger with Japan’s Nippon Steel to combat its escalating challenges. As the company faced dwindling fortunes, the deal promised essential funding for modernizing its aging mills. However, President Biden's recent blockade of the $14 billion acquisition on national security grounds—backed by a vocal opposition from President-elect Donald Trump—has left U.S. Steel with few viable paths forward.
Consequences of the Merger Failure
This merger was critical, as U.S. Steel warned that without it, the company would be compelled to close its steel plants and lay off countless workers, jeopardizing both livelihoods and entire communities reliant on these facilities. The options left are limited: pursuing a merger with another competitor poses potential antitrust issues, while lagging behind in adopting modern production technologies severely hampers the company’s competitiveness.
U.S. Steel's Response
Despite the standstill, U.S. Steel remains determined. In a bold move, the company, alongside Nippon Steel, is suing the federal government, claiming political interference skewed the review process. According to Amanda Malkowski, a spokesperson for U.S. Steel, “Nippon Steel and U.S. Steel remain confident that the transaction is the best path forward to secure the future of U.S. Steel.”
Current Standing in the Steel Industry
Currently, U.S. Steel dominates the production of flat-rolled sheet steel, essential for industries ranging from automotive to appliances. However, the company has succumbed to formidable foreign competition, especially from China, which now holds a dominating position in the global steel market. Once hailed as the world’s largest steel producer, U.S. Steel plummeted to 24th globally by 2023, trailing behind industry giants such as Baowu and Nippon Steel.
Impact of Tariffs and Market Dynamics
The U.S. steel industry saw a temporary boost from protective tariffs during the Trump administration, coupled with an aggressive construction boom, which drove steel prices to historic highs. However, skepticism about U.S. Steel’s long-term health persists, largely due to its slower transition compared to domestic competitors like Nucor, which has embraced more energy-efficient and cost-effective production methods.
Recent Developments in Production
In 2023, U.S. Steel made a significant, albeit late, stride by opening a new electric furnace plant in Arkansas. Yet, it emphasizes that only Nippon Steel can provide the investments necessary for substantial upgrades to critical facilities, including over $1 billion earmarked for the Mon Valley Works near Pittsburgh.
Union Concerns and Future Options
Against this backdrop, the United Steelworkers union, representing thousands of U.S. Steel employees, has firmly opposed the Nippon merger, accusing the Japanese company of unfair trade practices. The union's distrust is further fueled by its past advocacy for a merger with Cleveland-Cliffs, an American firm offering a labor-friendly environment.
Potential Consequences of a Merger with Cleveland-Cliffs
Should U.S. Steel consider aligning with another homegrown competitor, such as Cleveland-Cliffs, it would likely face intense scrutiny from federal regulators concerned about antitrust issues, given that these companies currently represent half of the domestic steel output. John Newman, a Miami law professor and former FTC official, indicates that such a merger could encounter significant legal challenges.
Political Considerations and Market Control
Federal regulators may weigh the argument that a consolidated domestic steel entity would better compete internationally, especially under a Republican administration. "There’s a political concern that we can’t let U.S. Steel falter,” notes Alden Abbott from the Mercatus Center.
Economic Implications of a Dominant Steel Producer
All eyes are also on the potential economic impact of one entity controlling a larger share of the domestic steel market, with experts arguing it could lead to rising costs for key industries, including defense. Sarah Bauerle Danzman from the Atlantic Council has highlighted the importance of diversifying steel production to stabilize prices.
Trump's Stance on U.S. Steel's Future
As the turmoil continues, Trump has urged U.S. Steel to resist being sold, arguing that tariffs will yield greater profitability and claiming, “Why would they want to sell U.S. Steel now when Tariffs will make it a much more profitable and valuable company?”
Historical Context of Tariffs in the Steel Industry
For the past several administrations, importing inexpensive steel has been a contentious topic, with tariffs historically utilized to protect the domestic industry. While tariffs have succeeded in preserving jobs, critics argue they have failed to enhance productivity or global competitiveness, emphasizing the pressing need for investments in innovative technology.
Conclusion
As U.S. Steel faces unprecedented uncertainty, the decisions made in the upcoming months will profoundly affect not only its future but the wider American steel landscape. The stakes are extraordinarily high—both for the company and the workers who are deeply intertwined with its destiny.



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)