Unveiling Antarctica: 85 New Subglacial Lakes Discovered!
2025-09-20
Author: Lok
A Hidden World Beneath the Ice
Beneath the vast ice sheets of Antarctica lies a secret network of dozens of subglacial lakes, integral to understanding the dynamics of Earth's largest ice mass. These lakes play a pivotal role in glacier movement and stability, ultimately affecting global sea levels.
A Groundbreaking Discovery
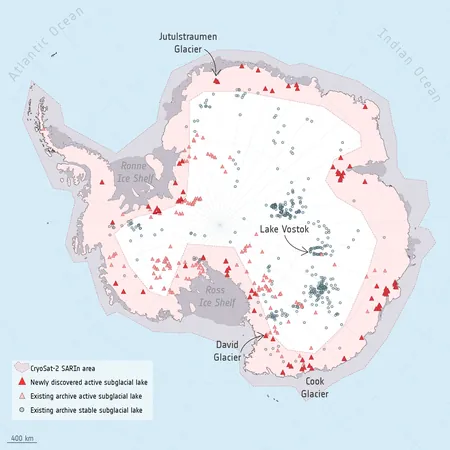
Thanks to a decade’s worth of data from the European Space Agency's CryoSat satellite, scientists have just identified 85 new subglacial lakes hidden beneath the frigid surface surrounding the South Pole. This discovery boosts the count of known active lakes below Antarctica to a staggering 231, revolutionizing our understanding of these icy formations.
Why Are These Lakes So Important?
Published in *Nature Communications*, this vital research highlights the cyclical nature of subglacial lakes, which periodically fill and drain. These events offer a unique glimpse into conditions deep beneath the ice, revealing new drainage pathways and interconnected lake networks.
Satellite Technology: A Game Changer
Lead author Sally Wilson from the University of Leeds emphasizes the challenge of observing these lakes: they are buried under hundreds of meters of ice, making research difficult. Before this study, only 36 complete filling and draining cycles had been recorded worldwide. Now, with 12 additional complete cycles observed, the total jumps to 48.
Data from the Past Decade
The CryoSat satellite, launched in 2010, has been instrumental in shedding light on these subterranean lakes. Utilizing its radar altimeter, researchers can monitor minute changes in ice surface height to map the existence and behavior of these lakes over the years.
A Dynamic Hydrology System
Co-author Professor Anna Hogg comments on the fascinating findings, stating, 'The fact that lake areas can shift during different cycles signifies a much more dynamic Antarctic hydrology than previously believed.' Continuous monitoring is essential as these lakes evolve.
What Lies Beneath—the Formation of Subglacial Lakes
These lakes form through geothermal heat and friction from sliding ice, pooling beneath the ice sheet before periodically draining. Not only does this reduce friction, but it also allows ice to slide more rapidly toward the ocean—a significant factor in sea level rise.
The Monolith: Lake Vostok's Impact
Among these lakes, Lake Vostok stands out as the largest, holding between 5,000 and 65,000 cubic kilometers of water beneath 4 kilometers of ice. Its stability is critical; if disrupted, it could influence Antarctic ice integrity, ocean currents, marine ecosystems, and global sea levels.
Future Predictions and Climate Modeling
Understanding the behavior of these subglacial lakes is crucial for refining ice sheet and climate models. Sally notes, "Subglacial hydrology is a missing piece in many of our models. By accurately mapping these lakes, we can better predict their influence on ice dynamics and future sea level changes."
The Road Ahead
As researchers continue to explore these enigmatic lakes, their findings will be vital for improving climate models and preparing for the implications of climate change on polar regions and beyond.




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)