Unlocking the Secrets of Lifespan: Why Some Animals Thrive for Centuries While Others Fade in Days
2025-05-24
Author: Wai
A Tale of Two Lifespans
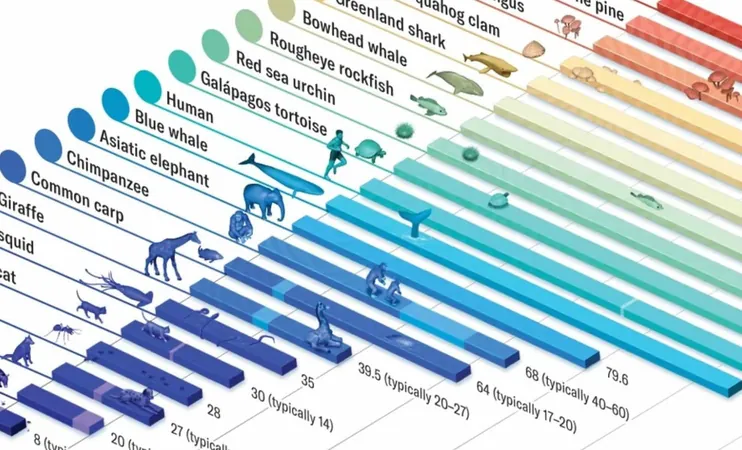
In the grand tapestry of life, some creatures come into existence, flourish, and vanish within mere days, while others soar through the ages, seemingly untouched by time. Scientists are racing against the clock to unravel the mysteries behind the astonishing lifespan disparities among species.
The Quest at the University of Birmingham
At the forefront of this fascinating inquiry is João Pedro de Magalhães, a molecular biologist at the University of Birmingham, leading the pioneering Human Ageing Genomic Resources program. His team meticulously curates the AnAge database, a comprehensive repository cataloging the maximum lifespans of countless animals.
The Mystery of Ageless Wonders
According to insights from Scientific American, Magalhães' groundbreaking research shines a spotlight on species that seem to defy the aging process. Some turtles, fish, and salamanders display no signs of aging as they mature. In a perfect world, free from predators and diseases, these extraordinary animals could theoretically continue living for decades—or even centuries!
Evolution: The Key Players in Lifespan
But why is there such a wide spectrum of aging across the animal kingdom? As Magalhães notes, "It’s a biological mystery why some species age faster than others." One intriguing lead points to the pressures of natural selection. Species that face high predation often evolve to mature rapidly and reproduce at a younger age, sacrificing longevity as a trade-off. Consider mice: they grow up in a hurry and meet untimely ends long before they encounter age-related threats like cancer.
The Long-Lived Survivors
On the flip side, longer-lived species tend to inhabit environments with fewer predators and more stability. Take the Greenland shark, for instance, which basks in the chilly North Atlantic and takes an impressive 150 years to reach sexual maturity. Unburdened by natural enemies and environmental upheaval, these sharks can afford to take their time, investing in slow aging and a deep-seated survival strategy.
DNA: The Lifesaving Code
An equally compelling factor in this longevity puzzle lies in the body's innate ability to repair DNA. Species with extended lifespans exhibit robust mechanisms for preserving genetic stability and thwarting mutations that lead to illnesses like cancer. Mice, however, don't share such luxuries. In captivity, they face high cancer rates because their evolutionary biology never prioritized long-term DNA maintenance.
Conclusion: Nature's Enigma
As scientists delve deeper into these enigmatic life cycles, the secrets of longevity slowly become clearer. Understanding why some species enjoy lengthy existences while others flicker out in an instant not only intrigues biologists but also holds potential implications for human health and aging. Who knows what revelations lie ahead?




 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)