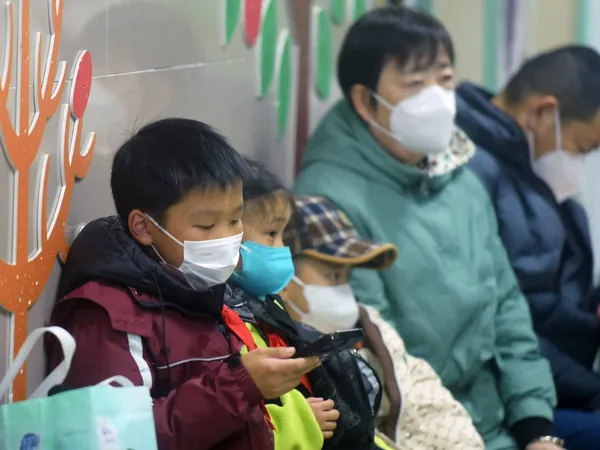

The Unseen Threat: What You Should Know About HMPV, the Respiratory Virus Taking Over China
2025-01-08
Author: Yan
In recent months, a respiratory virus known as human metapneumovirus (HMPV) has surged in China, predominantly impacting children and igniting fears of its potential spread beyond borders. As cases have spiked, especially in early December, health authorities are keen to monitor the situation closely, drawing comparisons to the global outbreak of COVID-19 that began in the region five years ago.
Understanding HMPV
Identified for the first time in 2001 in the Netherlands, HMPV is relatively common, with nearly every child being infected by the age of five. It shares similar transmission patterns with other respiratory viruses like influenza and COVID-19 and typically peaks during late winter and spring, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Transmission and Symptoms
HMPV spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes, and it can also be contracted by touching contaminated surfaces. Symptoms resemble those of the common cold or flu, appearing within three to six days post-infection. They commonly include:
- Cough - Fever - Nasal congestion - Wheezing - Breathlessness - Sore throat
While most individuals experience mild symptoms that resolve within a week, more severe complications can occur, particularly in high-risk groups such as infants, older adults, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
A Rise in Global Cases
Not just confined to China, HMPV cases have also been confirmed in India, where seven cases have been reported across various states, including Karnataka and Maharashtra. Officials are urging the public to remain vigilant, emphasizing standard preventative measures like handwashing and avoiding close contact with others.
Meanwhile, in the UK, laboratory data showed a 4.5% positivity rate for HMPV in tests conducted between December 23 and 29, hinting at seasonal patterns similar to those observed in other countries. Yet, comprehensive global data remains sparse, as HMPV does not receive the same level of surveillance as influenza or COVID-19.
Is HMPV Deadly?
While HMPV is highly contagious, it's rarely fatal in healthy individuals. The WHO has noted that the case mortality rate for HMPV is "very, very low." Most people recover fully within seven to ten days. However, in low-resource settings where healthcare access is limited, HMPV-related deaths have been reported more frequently.
Severe respiratory complications such as bronchitis or pneumonia can occur, especially in vulnerable populations. Infants are particularly at risk due to their smaller airways and developing immune systems, while older adults and those with pre-existing health conditions may also be more severely affected.
Current Treatment and Future Outlook
Currently, there is no specific antiviral treatment or vaccine for HMPV. Management largely focuses on alleviating symptoms through hydration, rest, and medications to reduce fever. Severe cases necessitate hospitalization and supplementary care, such as oxygen therapy.
As health authorities continue to monitor the situation, both the public and healthcare systems are urged to stay informed. Preparing for potential outbreaks and mitigating them through established public health responses will be crucial in the coming months.
With the world still recovering from the pandemic, the quick rise of HMPV serves as a stark reminder of the unpredictability of respiratory viruses. Stay alert and safeguard your health – the unseen threat of HMPV might be closer than you think!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)