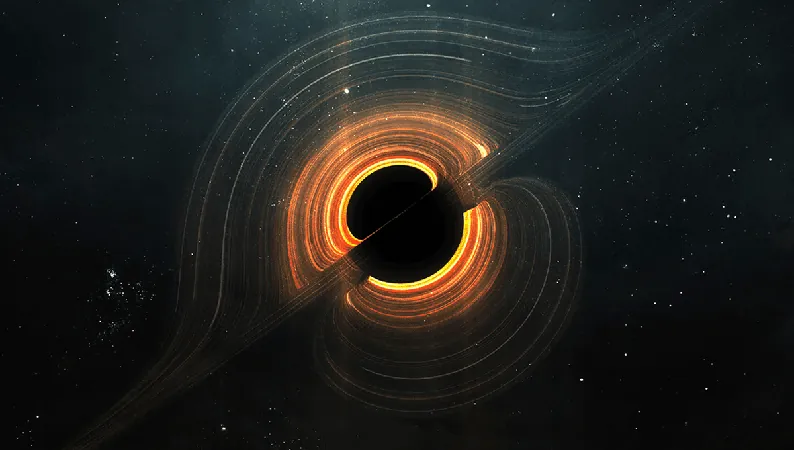

The Shocking Truth About Our Universe: Is the Big Bang Just the Beginning?
2025-06-07
Author: Ken Lee
A New Perspective on Cosmic Origins
For decades, we believed our universe sprang forth from a singular event known as the Big Bang. This model suggested that everything we see today emerged from an infinitely dense point. Yet, recent revelations shake the foundations of this theory.
Edwin Hubble’s Groundbreaking Discoveries
In the 1920s, astronomer Edwin Hubble made waves by observing that distant galaxies were moving away from us, indicating that the universe was expanding. This observation set the stage for the Big Bang theory, supported by the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB), the faint glow believed to be the universe's first light.
Challenging the Big Bang Model
However, prominent physicists argue that the Big Bang model is fraught with issues, particularly its reliance on a singularity—a point where the laws of physics break down. In a thought-provoking piece, Enrique Gaztanaga, an astrophysicist at the University of Portsmouth, boldly states, "This is not just a technical glitch; it's a deep theoretical problem that suggests we don't really understand the beginning at all."
A Revolutionary Approach
In their latest research, Gaztanaga and his team propose a new model that deviates from traditional thinking. Instead of focusing on cosmic inflation and mysterious dark energy, they explore what happens when an excessively dense region of matter collapses under its own gravity. This concept hinges on the Pauli exclusion principle, which states that no two identical particles can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously.
The Bounce Theory: A Game Changer
Their findings suggest that, rather than ending in a singularity, the gravitational collapse leads to a 'bounce.' Gaztanaga explains, "We show that this rule prevents the particles in the collapsing matter from being squeezed indefinitely. As a result, the collapse halts and reverses. The bounce is not only possible – it’s inevitable under the right conditions." This could reshape our understanding of cosmology!
A Universe Like Ours, But Different
The model posits that after this bounce, what emerges resembles the universe we inhabit today. Importantly, it inherently produces the two phases of cosmic expansion—inflation and dark energy—without needing hypothetical fields or additional speculative theories.
Testability: The Key to Acceptance
What sets this model apart is its testability. The scientists predict the universe has a slight positive curvature, suggesting that space isn’t flat. This could be verified through future cosmological surveys, such as the European Space Agency's upcoming Arrakihs mission.
A New Understanding of Our Place in the cosmos
If validated, this model could radically alter how we perceive our existence. Gaztanaga concludes, "Our entire observable universe lies within a black hole formed in some larger 'parent' universe. We are not special; we are part of a cosmic cycle shaped by gravity and quantum mechanics." As we stand on the brink of this new understanding, the implications for our place in the cosmos could be monumental, illuminating the path of not just where we came from, but where we are headed next!

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)