Supernovas: The Universe's Most Potent Particle Colliders?
2025-05-25
Author: Kai
A Cosmic Revelation!
In a groundbreaking discovery, scientists propose that supernovas could outshine even the most advanced particle colliders known to humanity. New research reveals these catastrophic stellar explosions can transform into extraordinary accelerators of particles, but only under specific conditions.
Cosmic Rays: The Mysterious Messengers
For decades, researchers have been captivated by cosmic rays—high-energy particles from beyond our galaxy that shower the Earth every second. Comprised mainly of protons, these cosmic travelers pack a punch, sometimes reaching energies that exceed a staggering one peta-electron volt (PeV)—about a thousand times more potent than the Large Hadron Collider's most energy-packed collisions.
The Power Behind the Explosion
Astronomers have long speculated that these high-energy cosmic rays originate from the explosive demise of massive stars—supernovas. These celestial fireworks hold the perfect ingredients for creating such extreme energy: an explosive detonation, a torrent of elementary particles, and powerful magnetic fields ready to unleash chaos.
A Puzzle of Expectations
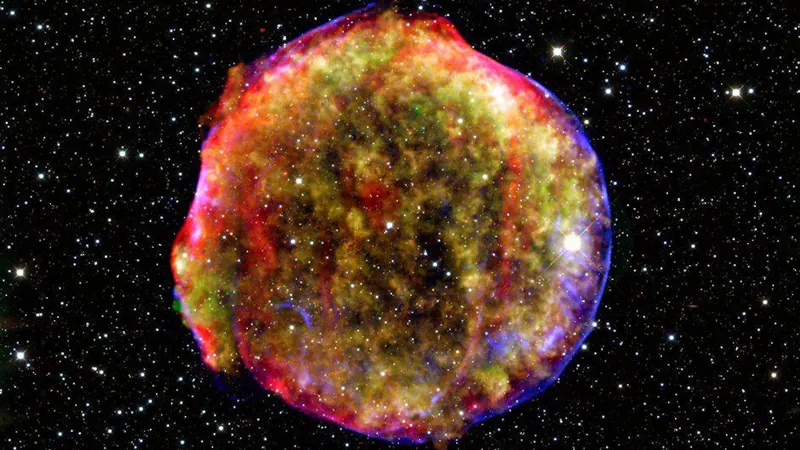
However, studies of nearby supernova remnants like Tycho and Cassiopeia A revealed a surprising twist: the cosmic rays emanating from these sites were far weaker than predicted. This conundrum puzzled scientists and left the supernova hypothesis hanging in the balance.
Resurrecting the Supernova Hypothesis!
A new paper published in *Astronomy & Astrophysics* breathes new life into the supernova narrative. Researchers propose that certain supernova remnants, under specific circumstances, can indeed act as "PeVatrons"—powerful cosmic ray factories capable of producing cosmic rays at the elusive PeV level.
Key Ingredients for Success
The study highlights that before a star goes supernova, it must shed a significant amount of mass—at least two suns’ worth—while ensuring that this material remains dense and closely packed. This paves the way for a powerful explosive aftermath.
The Dance of Particles
When the supernova erupts, the shockwave crashes into the surrounding dense material, ramping up magnetic fields to astonishing strengths. These conditions excite random subatomic particles, accelerating them within the chaotic shockwave. Each collision amplifies their energy, eventually allowing some to escape the turmoil and stream into space.
A Temporary Burst of Energy
However, this particle accelerative frenzy is short-lived; as the shockwave wanes within months, it may still produce many cosmic rays but rarely maintains the PeV threshold. This leads scientists to wonder about the vast potential still hidden within these stellar explosions.
The Cosmic Frontier Awaits!
The exploration of supernovas as colossal particle accelerators opens a thrilling new frontier in astrophysics, inviting further investigation into the mysteries of cosmic rays and the forces that govern our universe. Could these stellar explosions be the key to unraveling even greater cosmic secrets?


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)