
SpaceX Dragon Achieves Historic Orbit Boost for the International Space Station!
2024-11-08
Author: Wai
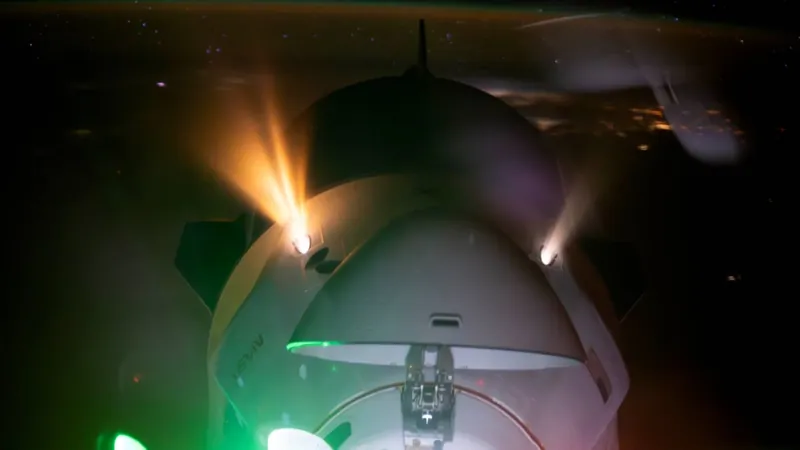
In a groundbreaking achievement for commercial spaceflight, SpaceX's Dragon spacecraft has successfully performed its first orbital boost to enhance the altitude of the International Space Station (ISS). This event, which took place on November 8, 2023, marks a significant milestone in the history of the ISS.
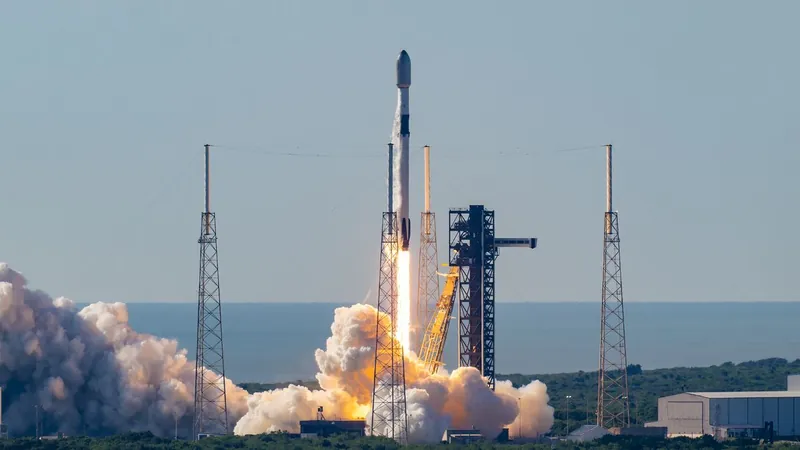
The boost was part of SpaceX's 31st commercial resupply mission, which launched on November 4. After the Dragon cargo vehicle successfully docked with the ISS, it began operations to stabilize the station’s trajectory in low-Earth orbit. This maneuver is essential, as the ISS requires periodic boosts to maintain its orbit, preventing it from descending into Earth's atmosphere. Historically, such operations relied on Russian spacecraft like Soyuz and Progress; however, Dragon's involvement represents a shift towards greater reliance on American technology.
NASA announced the successful ignition of Dragon's thrusters at approximately 12:50 PM ET (1750 GMT), which lasted about 12.5 minutes. The maneuver not only enhanced the ISS's orbit but also provided critical data for developing a future deorbiting vehicle. This vehicle, set to be constructed by SpaceX, will ultimately guide the decommissioned station into a controlled descent into the Pacific Ocean post-2030.
While this event celebrates new capabilities, it also serves as a reminder of the aging technology of the ISS. With continuous operation for nearly 25 years, the space station's viability is being reassessed as NASA anticipates its retirement, citing increasingly daunting maintenance costs and technological obsolescence. However, plans are underway for a new era of commercial space stations, expected to sustain NASA's research efforts in low-Earth orbit after the ISS's decommissioning.
In a recent press conference, Jared Metter, SpaceX's director of flight reliability, remarked on the significance of this successful maneuver. He stated, “Today’s attitude control maneuver was a good demonstration of Dragon’s capabilities,” highlighting how this operation lays the groundwork for future projects aimed at the ISS’s retirement.
Interestingly, although geopolitical tensions have escalated since Russia's actions in Ukraine in 2022, collaboration between the U.S. and Russia at the ISS level continues. Nonetheless, Dragon's success signifies a reduced dependency on Russian resources for the operational upkeep of the ISS—a critical factor considering the current global landscape.
The importance of this operation cannot be overstated. Since the retirement of the space shuttle in 2011, NASA astronauts were reliant on Russian spacecraft to reach the ISS. The introduction of SpaceX's Crew Dragon in 2020 not only restored American crewed access to the station but now also demonstrates the ability to sustain its orbit, paving the way for future exploration and scientific discovery.
As we advance towards exciting new frontiers in space, one thing is clear: SpaceX’s Dragon is not just a part of history but is actively shaping the future of space exploration! What other capabilities will this game-changing spacecraft unveil in the coming years? Stay tuned!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)