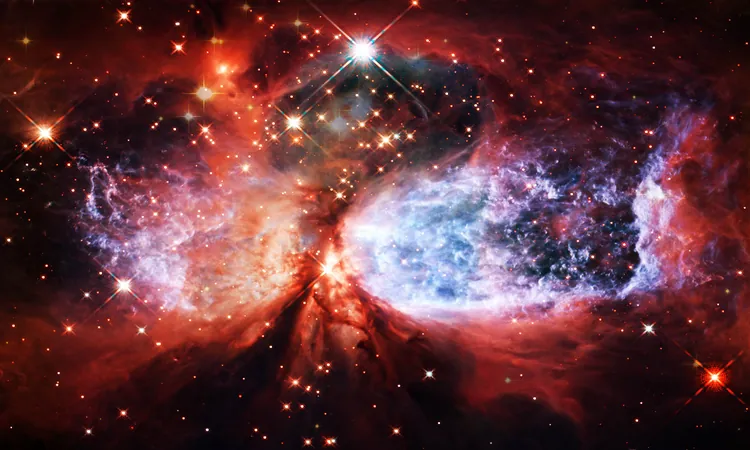

Shocking Discovery: The Universe's Expansion Rate is Clashing with Scientific Predictions!
2025-01-17
Author: Wei
Introduction
The quest to understand the Universe's expansion has perplexed scientists for decades, and recent findings have escalated concerns among researchers. New measurements indicate that galaxies are drifting apart faster than previously anticipated, leading many experts to question the adequacy of the standard model of cosmology.
Historical Context
For context, it was Edwin Hubble who first discovered the expansion of the Universe in 1929, proposing that the rate of expansion, now known as the Hubble constant, merits intensive scrutiny. Each generation has attempted to determine this rate with increasing precision, aiming to decipher how cosmic structures evolve over time.
Hubble Tension
Despite advancements, a growing dilemma known as "Hubble tension" has emerged, stemming from two divergent approaches to measurement: local observations of galaxy distances and analyses from the early Universe. The results from these investigations have begun to diverge alarmingly, prompting remarks from Dan Scolnic, an associate professor of physics at Duke University, who stated, "The tension now turns into a crisis."
Nature of the Conflict
So, what is the nature of this conflict? The discrepancy arises when researchers compare cosmic observations at vastly different distances. While standard theories suggest a gradual expansion rate, measurements from local galaxies indicate a significantly quicker pace, akin to comparing a child's growth chart with expected developmental milestones—yet, the actual growth trajectory isn’t aligning with predictions.
Cosmic Ladder and DESI
To shed more light on the situation, scientists have utilized a "cosmic ladder" to accurately measure celestial distances, thereby constructing a reliable framework to support these expansive investigations. A pivotal project called the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) recently contributed to this effort by providing a comprehensive database of galaxy distances, enhancing precision in the process.
Coma Cluster and Supernovae
Scolnic emphasized the need for accurate anchors, pointing towards the Coma Cluster—a region of contention among researchers for the last 40 years. By examining light patterns from 12 Type Ia supernovae—known for their consistent brightness—Scolnic's team determined the Coma Cluster resides approximately 320 million light-years away, positioning their measurement amidst previous computations over the decades.
The Hubble Constant
The crux of the matter will be the newly calculated Hubble constant: 76.5 kilometers per second per megaparsec, indicating how galaxies are receding from each other with every 3.26 million light-years of separation. This value resonates closely with localized findings, reinforcing the idea that the Universe is expanding at an accelerated pace—more swift than conventional theories allow.
Broader Implications
Crucially, this engaging debate around the Hubble constant poses larger questions about the underlying principles of cosmology. Some scientists believe the anomaly signals a need for adjustments in theoretical models, while skeptics urge a meticulous re-evaluation of the measurements themselves.
Future Observations
As state-of-the-art telescopes and novel observational techniques emerge, a wealth of fresh data can only deepen our understanding of cosmic expansion. "We're at a turning point where we could reshape our understanding of the Universe," Scolnic noted, hinting at the exhilarating possibilities ahead in cosmological studies.
Conclusion
Beyond the immediate calculations, profound questions linger about dark energy, dark matter, and the potential for unknown factors influencing the Universe's behavior. As future observations roll in from observatories around the globe, researchers remain vigilant, determined to decode truths hidden amongst the cosmic mysteries.
Final Thoughts
The adventure of understanding the universe's expansion is far from over, with each new discovery potentially rewriting our cosmic narrative. Are we on the brink of a revolutionary breakthrough in astrophysics? Only time will tell!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)