Revolutionary Breakthrough: Scientists Create Photosynthesizing Animal Cells!
2024-11-09
Author: Kai
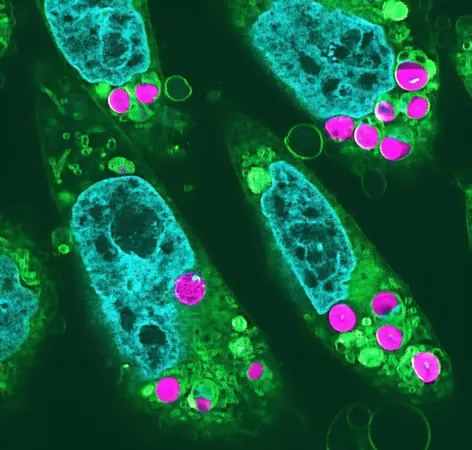
In a groundbreaking scientific achievement, researchers at the University of Tokyo have successfully engineered animal cells capable of performing photosynthesis. This remarkable development, led by Professor Sachihiro Matsunaga, has the potential to reshape medical research and revolutionize lab-grown meat production, paving the way for sustainable food and innovative medical solutions.
What is Photosynthesis and Why Does It Matter?
Photosynthesis is a process traditionally reserved for plants, algae, and some bacteria, allowing them to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen. This process is vital not only for plant growth but also for maintaining the balance of gases in our atmosphere—producing the oxygen necessary for human survival.
Animal Cells and Photosynthesis: A Scientific Dilemma
Historically, attempts to infuse animal cells with the ability to photosynthesize have failed for over 50 years. Matsunaga explained that animal cells typically consume oxygen and break down sugars—a process opposite to photosynthesis. However, by introducing photosynthetic capabilities to these cells, researchers hope to create organisms that consume less oxygen and produce their own energy, thereby reducing carbon dioxide emissions.
Overcoming Historical Challenges
The team overcame significant obstacles that had previously stalled research in this area. They focused on finding chloroplasts—structures responsible for photosynthesis in plants—that could survive in the warmer temperatures of animal cells. Moreover, the researchers devised a novel method to allow animal cells to ingest chloroplasts, treating them as food, which prevented the immune response that would normally reject them.
Unexpected Results and Future Applications
To their astonishment, the modified animal cells not only tolerated the chloroplasts but also exhibited increased growth rates, indicating that these cells can utilize the energy produced via photosynthesis. This breakthrough could have a profound impact on medical research, particularly in enhancing oxygen delivery in tissue cultures, a frequent challenge in developing lab-grown organs and meats. Matsunaga sees potential applications where implanted cells could provide localized oxygen delivery, especially in patients with heart disease.
Looking Ahead: New Frontiers in Biological Engineering
This pioneering study signifies a paradigm shift in biological engineering, suggesting that photosynthesis could extend beyond plants and into the realm of animal cells. While researchers have yet to extend the duration of chloroplast function within animal cells, Matsunaga’s work opens up a horizon of possibilities—from improved food production techniques to innovative medical treatments tailored for specific organs.
As Matsunaga puts it, 'This breakthrough underscores the transformative potential of photosynthesis across biological entities, presenting unique solutions to some of humanity's greatest challenges concerning food production and health care.'
With this discovery, the scientific community is poised at the cusp of a new era, where the boundaries of biological capabilities are being pushed further than ever before. Stay tuned as we continue to explore advancements in this fascinating field!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)