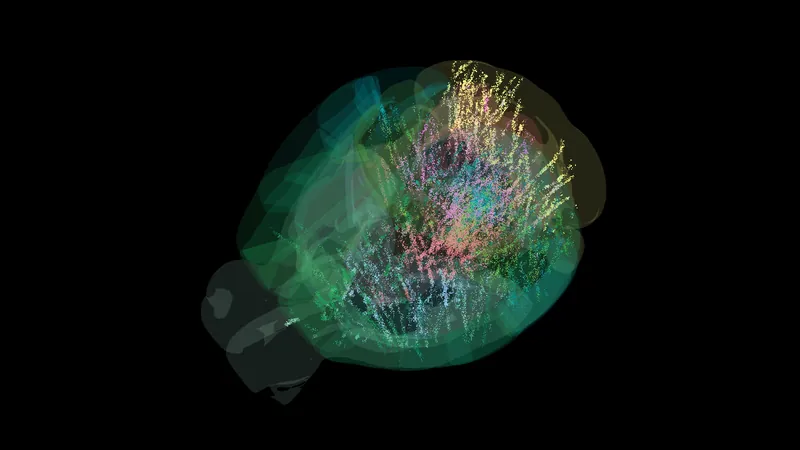
Revolutionary Brain Mapping Study Redefines Decision-Making
2025-09-04
Author: Ming
Mapping the Mind: A Groundbreaking Research Effort
In a historic breakthrough, researchers have unveiled the first comprehensive activity map of a mammalian brain, fundamentally changing our understanding of how decisions are formulated. This collaboration, involving a consortium of scientists from multiple labs across Europe and the U.S., analyzed data from over 600,000 mouse brain cells, covering a staggering 95% of the brain.
Unified Approach to Brain Research
Chaired by the International Brain Laboratory (IBL), this monumental project sought to tackle ongoing inconsistencies in previous neuroscience studies. Recognizing a shared frustration among researchers about disparate methods and findings, IBL scientists pooled resources to conduct a standardized experiment that no single lab could achieve alone.
A Collective Effort of Innovation
Using 139 mice implanted with advanced Neuropixels probes—capable of recording up to 1,000 neurons simultaneously—the research team designed an experiment that measured brain activity during a straightforward task. The mice were rewarded for accurately responding to a flashing visual cue, providing a controlled environment for the labs to replicate.
Shattering Conventional Wisdom on Decision-Making
Traditionally, textbooks suggested a linear pathway of brain activity during decision-making: first, the visual cortex activates, followed by the prefrontal cortex, and then motor regions respond. Interestingly, while the initial activation in the visual cortex aligned with expectations, the study revealed decision-making signals distributed across a broader range of brain regions than anticipated.
A Surprising Spread of Brain Activity
The startling discovery was that the decision signals were not confined to specific areas but were widely present throughout the brain. Even during trials where visual cues were faint, requiring the mice to make educated guesses, the range of brain activity deepened the mystery of how past experiences influence decisions.
Inspired by Astronomy: A New Era of Neuroscience
The innovative methodology mirrors the collaborative efforts seen in the worlds of particle physics and genomics. Carandini, a lead researcher, likened the project’s impact to the advancement of telescopes in astronomy, which allowed us to explore the cosmos in rich detail rather than just observing distant stars in isolation.
What's Next for Neuroscience?
While these findings provide a groundbreaking view of decision-making processes, they remain correlational. The next big step in neuroscience, according to Carandini, is to establish a causal relationship between brain activity and decision-making—a challenge he describes as the next frontier in understanding the complexities of the brain.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)