
Massive 'Red Monsters' Discovered: A Cosmic Revelation That Changes Everything!
2025-05-05
Author: Ming
Astronomers have experienced a groundbreaking twist in cosmic discovery! The Webb Telescope, renowned for its deep-field imaging, has identified enormous ‘red monster’ galaxies that sparkled to life just 500 million to one billion years after the Big Bang. This unexpected revelation is reshaping our understanding of how galaxies form.
The Surprising Discovery of Cosmic Giants
While scientists anticipated a slow emergence of faint, young galaxies, they were instead greeted with these gigantic and vibrant red galaxies, challenging the established cosmic timeline. These colossal entities are comparable to our Milky Way, prompting researchers to reconsider longstanding theories regarding the evolution of galaxies.
Three Giants Break All the Rules
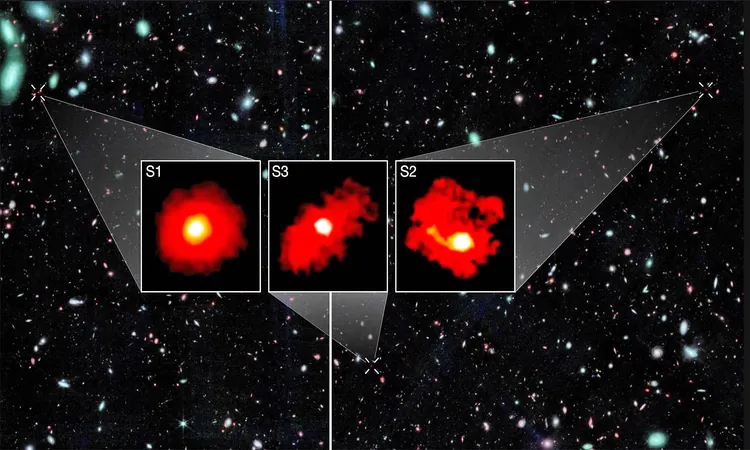
An international team delved into the Webb Telescope’s FRESCO survey, meticulously analyzing its imagery and spectroscopic data. Their examination of 36 galaxies revealed that most adhered to the expected behaviors predicted by the Lambda Cold Dark Matter (ΛCDM) framework. However, three remarkable galaxies stood out, each boasting stellar masses exceeding 10 billion times that of the Sun, which is astonishingly high for the universe's formation period.
Fueling Star Formation Like Never Before
Collectively, these three titans are believed to have contributed to a staggering 17 percent of all star formation during the universe's early years, specifically between redshifts 5 and 6. Their ineffable efficiency caught the team’s attention; they appear to have converted half of the normal matter in their dark matter halos into stars—a feat two to three times greater than that of typical galaxies.
What Makes Them 'Red Monsters'?
These ‘red monsters’ earned their name due to their high dust content, which causes them to appear red in the near-infrared spectrum captured by the Webb Telescope. This unique visibility, facilitated by Webb’s NIRCam/grism setup, allowed astronomers to explore star-forming regions obscured by dust that blocked earlier observational methods reliant on ultraviolet light.
A Game-Changer for Cosmic Understanding
This discovery compels scientists to re-examine the ΛCDM model, which typically suggests that only a fraction of gas is used to form stars in galaxies over billions of years. These red monsters suggest that enhanced early conditions—such as higher gas densities or more efficient mergers—could drastically alter our perception of cosmic growth.
The Cosmic Time Machine
The Webb Telescope operates as a cosmic time machine, allowing us to see the universe as it was 13 billion years ago. This peering back into the depths of space forces theoretical frameworks to evolve as massive galaxies manifest much sooner than expected post-Big Bang.
What Lies Ahead?
With future Webb programs aiming to expand our understanding of early massive galaxies, alongside the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) enhancing observations of cold gas and dust, the quest continues. Will more 'red monsters' appear, further revolutionizing our theories? Perhaps the early universe was a far more dynamic and vigorous environment than ever realized!
As researchers continue to peel back the layers of cosmic history, we stand on the brink of an extraordinary new chapter in our understanding of the universe. The revelation of these red monsters is just the beginning of a thrilling journey into the depths of cosmic infancy!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)