
Is the Big Bang Theory on the Brink of Collapse?
2025-09-09
Author: Ling
The Origin of Our Universe in Question
Did the Universe truly begin with a bang? The age-old queries surrounding the Universe's inception and its eventual fate have been pivotal in cosmology. The once intractable mysteries seem to have found answers through the Big Bang theory, which has formed the bedrock of modern cosmology, gaining traction with a mix of scientific validation and cultural resonance.
Cracks in the Cosmic Foundation
Despite its grandeur, the Big Bang theory is under fire. While it offers an awe-inspiring narrative about the Universe's beginnings, it also leaves a flurry of perplexing questions unanswered. Recent astronomical observations cast shadows over its credibility, indicating that the theory may soon face a monumental crisis.
Hubble's Revelation: A Cosmic Perspective
The groundwork for the Big Bang theory was laid in 1929 when astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered that galaxies are moving away from us. This motion isn't by chance; the fabric of space itself is expanding, similar to how points on an inflating balloon drift apart. This expanding Universe suggested a beginning, implying that all matter erupted from a singular, immensely dense point nearly 14 billion years ago.
Problems Arise: Studying the Stars
Though the Big Bang laid a narrative foundation, it demanded further clarity. Early stars called Cepheid variables, once poorly understood, were later utilized to measure cosmic distances, helping refine the understanding of the Hubble constant, which measures the Universe's expansion. However, significant challenges remained as the theory struggled to account for the observable Universe.
The Missing Matter Mystery
Astounding as it may seem, calculations have revealed that the visible matter we can detect only accounts for about 5% of what is deemed necessary for the critical density of the Universe. Where is the rest? Theories suggest additional forms of matter, such as the elusive dark matter, yet even this does not paint the whole picture.
Dark Energy and Accelerating Expansion
Fast forward to the late 1990s, and astronomers made a groundbreaking discovery: the Universe's expansion was not slowing down; it was accelerating. This revelation brought the concept of dark energy to the forefront—a mysterious force counteracting gravity, potentially making up about 70% of the Universe. The implications? As the Universe stretches, it may approach a state of 'heat death'—an end where galaxies fade from view.
Challenging Cosmological Foundations
Despite earlier successes, the Big Bang theory now grapples with the 'Hubble tension'—a discrepancy between the predicted rate of expansion and observations made using supernovae. Teams of astronomers are racing to determine if this divergence signifies a genuine crisis or simply the need for a refined understanding of cosmic phenomena.
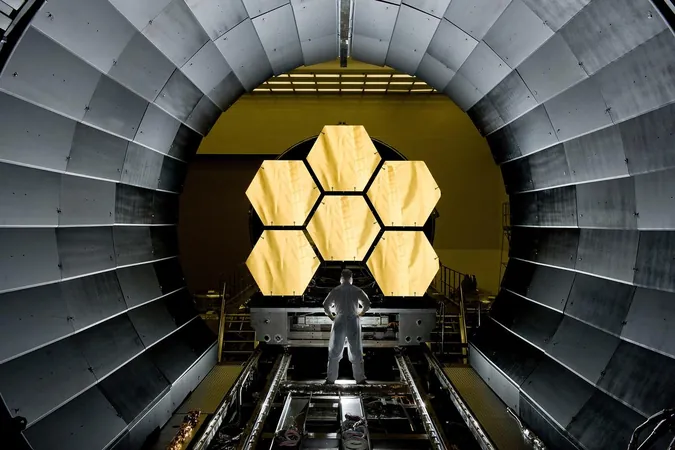
The Role of the James Webb Space Telescope
With the advent of the James Webb Space Telescope, scientists are peering back in time to when the first stars ignited. Yet, instead of spotting nascent galaxies, it's uncovering fully formed clusters too early for the models to predict. This predicament adds another layer of uncertainty to our understanding of cosmic history.
Theoretical Turbulence Ahead
As voices of dissent grow louder among cosmologists, the Big Bang theory's reliance on unverified concepts like cosmic inflation raises eyebrows. Critics argue that without empirical evidence for core elements, its long-standing status may be unjustified. In a climate of mounting skepticism, the theory's foundational stability appears precarious, leading some to call for a reconsideration of our cosmic narrative.
The Quest for Cosmic Truth
Despite its flaws, the Big Bang theory remains at the forefront of cosmology. However, history teaches us the peril of complacency in science. The journey to unravel the Universe's secrets is far from over, promising new insights and challenges ahead. As researchers delve deeper, Einstein's caution resonates: the validity of a theory is ever contingent on future discoveries.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)