Is a Spectacular Underwater Eruption Imminent? Scientists Warn of Growing Volcano off the West Coast!
2025-01-27
Author: Yan
Introduction
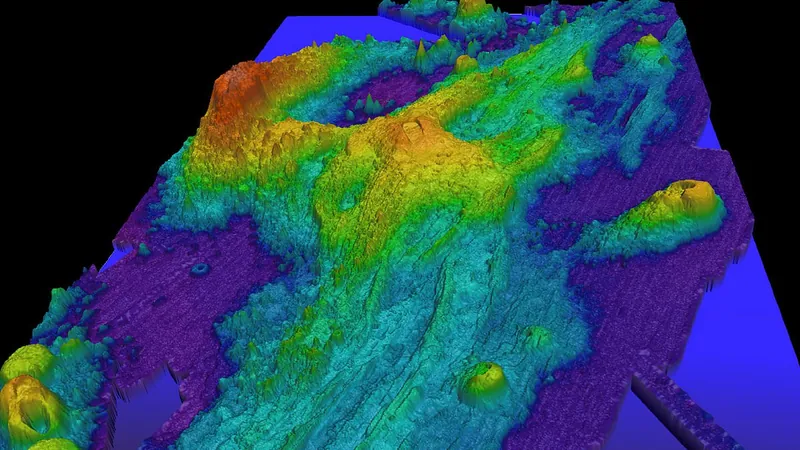
Prepare for an explosive revelation from the depths of the Pacific Ocean! Axial Seamount, an enormous underwater volcano situated nearly 300 miles off the Oregon coast, is currently exhibiting alarming signs of a potential eruption. Spanning a staggering 1.25 miles and towering 3,600 feet above the ocean floor, this giant sits 4,626 feet beneath the surface and is bubbling with volcanic activity.
Signs of Eruption
Experts are closely monitoring Axial Seamount as it continues to swell and rumble—a clear sign of magma accumulation, which has led scientists to predict an eruption before the curtain falls on 2025. However, worry not! Leading volcanologists assure us that this underwater phenomenon doesn’t pose a significant risk to surrounding areas.
Expert Insights
Volcanologist Mike Poland, from the Yellowstone Volcano Observatory, described Axial Seamount as perhaps "the best-monitored submarine volcano in the world." This monitoring gives researchers the unique opportunity to study ongoing volcanic behavior in real-time, a luxury not often afforded by land-based volcanoes.
Comparisons to Other Volcanoes
This young shield volcano, part of the Juan de Fuca Ridge, bears similarities to Mauna Loa in Hawaii, bringing the prospect of a non-explosive eruption. "When Axial Seamount erupts, imagine a Hawaiian lava flow—lava will gently emerge from the caldera, spreading seamlessly across the ocean floor," Poland explained.
Volcanic Activity and History
Bill Chadwick, an Oregon State University Research Associate, further emphasized the volcano's unique nature. With a record of three eruptions in the last 30 years, Axial is one of the most active volcanoes in the Pacific Northwest. He stated, "If it’s not erupting, it’s inflating, gearing up for its next explosive release."
Previous Eruptions
Axial Seamount's volcanic history includes major eruptions in 1998, 2011, and 2015, with evidence suggesting it has erupted numerous times before those recorded events. Following its last recorded eruption in 2015, the seafloor experienced an initial uplift of over a meter per year, but by 2023, that rate slowed significantly. Yet, due to recent observations, scientists are now seeing a rebound in inflation, reaching an impressive rate of 25 centimeters per year.
Inflation Dynamics
In an intriguing analogy, Chadwick remarked, “Axial’s summit inflates like a balloon as magma is supplied from below. At some point, the pressure becomes too great, leading to a crack and eventual magma flow to the surface.” This phenomenon mirrors volcanic behaviors seen globally, making Axial a focal specimen for scientific study.
Seismic Activity
The volcano’s seismic activity is also on an upward trend, with a significant increase in earthquakes detected just before its 2015 eruption—the skies above (or rather, the seas below) seem to herald Axial’s next dramatic performance.
Underwater Eruption Dynamics
Interestingly, the nature of underwater eruptions is drastically different. Axial Seamount lies beneath immense ocean pressure, which hinders the efficiency of explosive eruptions. As magma reaches the surface, it swiftly cools upon contact with freezing ocean water, creating a solidified crust that insulates the lava flow—a distinct mechanism that reduces its impact.
Monitoring Technology
To facilitate their monitoring, the OSU research team employs cutting-edge tools, including a remotely operated vehicle named Jason for underwater exploration. This technology allows for instantaneous data collection, letting researchers observe volcanic activity from the comfort of their offices. “I can look at my laptop and see data that was collected just 10 minutes ago,” Chadwick proudly remarked.
Safety and Research Opportunities
Despite its active nature, scientists stress there is no imminent threat to human life. “If you were to sail over Axial Seamount, you wouldn’t notice a thing unless you had specialized equipment,” Chadwick explained. This lack of immediate threat translates into a unique opportunity for researchers to study volcanic eruptions without the usual life-and-death stakes present with land-based volcanoes.
Future Implications
Chadwick envisions these eruption forecasts as groundbreaking scientific experiments that could inform future volcanic predictions worldwide. The extensive real-time monitoring of Axial Seamount positions it as a model for understanding volcanic behavior in our oceans.
Conclusion
As scientists prepare for potential eruptions, they remain dedicated to unlocking the mysteries of volcanology, using Axial as a crucial reference point that could enhance predictive models for other dynamic volcanoes, both on land and underwater.
Final Thoughts
Stay tuned! The scientific community is ready, and as Axial Seamount continues to stir beneath the waves, the world watches in anticipation of what could be an awe-inspiring natural spectacle!



 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)