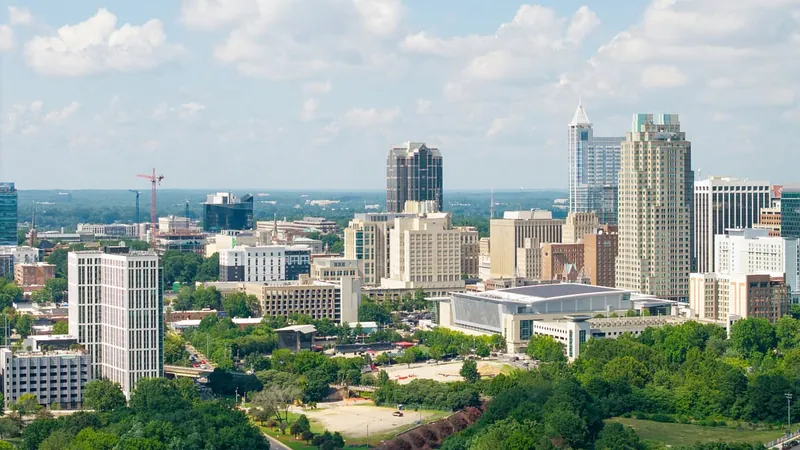

Chilling Alert: Deadly Tuberculosis Spreads from Maine to North Carolina High School
2025-09-08
Author: Chun
A Troubling Outbreak Hits the Classroom
In a shocking development, a case of the deadly lung disease tuberculosis (TB) has surfaced at Leesville High School in Raleigh, North Carolina, mere days after officials reported multiple TB cases in Maine. The alarming discovery comes just weeks into the new academic year for the school's 2,500 students.
Health Officials Swing into Action
Wake County officials confirmed that an active TB case was identified in an individual who had attended the school recently. While the person remains unnamed, health authorities are collaborating with Wake County Schools to track and inform anyone who may have been in close contact.
The Global Threat of Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis, labeled the deadliest disease worldwide by the World Health Organization, claims approximately 1.25 million lives each year—primarily in developing nations. The North Carolina case follows Maine’s announcement of three positive TB tests, each related to different sources, emphasizing the urgent need for vigilance.
An Increasing Trend in TB Cases
In the U.S., cases of tuberculosis are on the rise—recording 10,347 infections in 2024, a staggering 8% increase from the previous year and the highest count since 2011. Despite this, health officials assert that the risk to the general public remains low.
What Parents Need to Know
Parents at Leesville High School were alerted by the Wake County Health Department about a health situation impacting their school, although the notice did not explicitly mention TB. Those potentially exposed will receive direct notifications and further instructions for testing.
Facts and Figures on TB in North Carolina
The North Carolina Department of Health and Human Services reported 215 TB cases in the state for 2023, marking an increase from 164 cases in 2022. So far in 2025, 128 cases have been documented, highlighting a troubling trend.
The Fatality Rate of TB
Tuberculosis is known for its high fatality rate, with untreated cases leading to death in up to half of those infected. This stands in stark contrast to the mortality rates of diseases like COVID-19 and measles. Although TB has become significantly less deadly over the decades, it remains a serious health threat.
Understanding Transmission and Symptoms
TB is primarily transmitted through long-term, close contact with an infected individual, and Dr. Dora Anne Mills from MaineHealth reassured the public that casual interactions pose little risk. Early symptoms include a persistent cough, potential chest pain, and fever, progressing to severe complications if untreated.
Vaccination and Treatment
While the BCG vaccine can help prevent TB, it is not routinely offered in the U.S. The vaccine is mainly administered to children in developing countries, leaving a telltale scar as a sign of its effectiveness. Treatment options are available, primarily through a regimen of antibiotics.
Conclusion: Vigilance Is Key
As the outbreak unfolds, health officials urge communities to remain vigilant. Awareness and prompt action can mitigate the spread of this dangerous disease and protect vulnerable populations, particularly children and those with compromised immune systems.

 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)