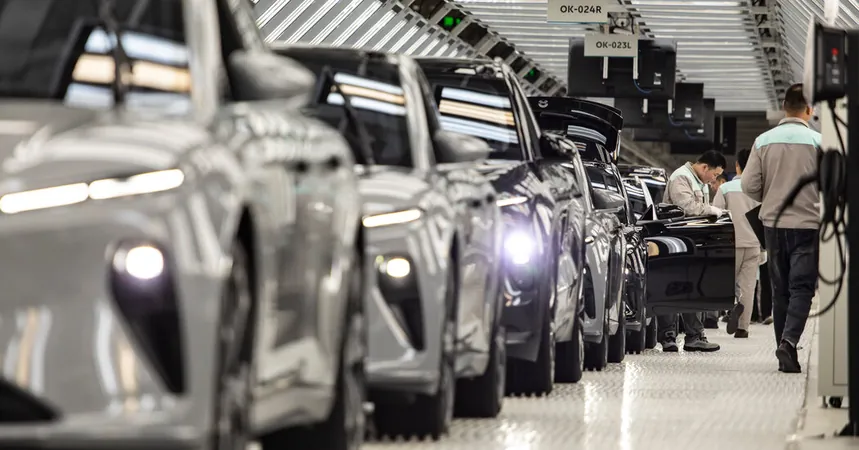

Biden Administration Targets Chinese Software in Vehicles: A National Security Initiative
2024-09-23
Introduction
In a bold move aimed at bolstering national security, the Biden administration announced on Monday a comprehensive ban on Chinese-developed software for internet-connected cars in the United States. This initiative seeks to safeguard U.S. interests by preventing potential surveillance and interference from Chinese intelligence agencies, which could exploit automotive electronics to access sensitive infrastructure, including the U.S. electric grid.
Background of the Initiative
This latest action builds on previous measures taken by the administration, including the ban on Huawei telecommunications equipment and scrutiny of Chinese-manufactured cranes operating in American ports. Coupled with Congressional efforts to force TikTok to sever ties with its Chinese owners, these measures underline a vigorous commitment to addressing perceived cyber vulnerabilities associated with Chinese technology.
Statements from Officials
National security adviser Jake Sullivan emphasized that national security—not politics—drives this proposed ban, suggesting it could be finalized before President Biden’s term concludes on January 20. Earlier this year, the Biden administration imposed 100 percent tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, labeling them as unfairly subsidized and asserting that these tariffs would protect American jobs.
Concerns Regarding Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles present new risks due to their extensive data collection capabilities, constantly communicating with personal devices, other vehicles, and critical infrastructure. “Many of these technologies collect large volumes of information on drivers,” Sullivan noted, highlighting how foreign-developed automotive components could create vulnerabilities.
'Volt Typhoon' Concerns
One significant concern is the so-called "Volt Typhoon," which U.S. intelligence officials allege is part of Chinese strategies to infiltrate critical infrastructure, potentially enabling malicious actions during geopolitical crises, such as a conflict over Taiwan.
Industry Impact and Bipartisan Support
While the current focus is on the automotive sector, officials are exploring which other industries may face similar software and hardware restrictions. The bipartisan apprehension surrounding Chinese technology indicates that concerns over national security are increasingly prioritized, although experts caution that such fears could impact American consumers negatively.
Proposed Scope of the Ban
Notably, the proposed ban would encompass all wheeled vehicles—including cars, trucks, and buses—while exempting those not used on public roads. The initiative aims to enforce a prohibition on Chinese and Russian software in connected vehicles starting with model year 2027, and extend to hardware integrated into vehicle connectivity systems by model year 2030.
Government's Proactive Approach
Commerce Secretary Gina Raimondo expressed the administration's proactive approach to securing Americans from potential surveillance threats, stressing that foreign adversaries could exploit connected vehicles to gather sensitive data. She warned of severe consequences, including possible territorial control of vehicles, leading to road blockages and accidents.
A Broader Trend in Policy
Emerging from heightened scrutiny, the proposed rule reflects a broader trend among U.S. policymakers to tighten control over foreign technology that poses security risks. After initiating an investigation into embedded Chinese technology in vehicles, the administration has also taken steps to restrict imports of Chinese cars to protect domestic manufacturing of clean energy products.
Tariffs and Domestic Manufacturing
Freshly quadrupling tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, the administration aims to deter imports that could threaten job creation in America, as the government pushes for the growth of its own clean energy industry—a move expected to cost hundreds of billions in the coming decade.
Challenges for U.S. Automakers
As U.S. automakers grapple with the complexities of high-tech integrations in vehicles, they face a double-edged sword. While aiming to access advanced technologies crucial for autonomous driving and safety features—many of which are produced in China—there’s an urgent need to balance innovation with national security imperatives. Meanwhile, China’s dominance in the electric vehicle market and battery production complicates the U.S. strategy, as half of new cars sold in China are electric, offering a rapid scaling advantage for Chinese manufacturers.
Conclusion
As the digital arms race escalates, the stakes continue to rise in a world increasingly defined by cyber capabilities and technological warfare. The Biden administration’s decisive actions may serve as a significant barrier against espionage while potentially reshaping the auto industry landscape in the U.S. and beyond.


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)