Are Chatbots Leading Us Toward a Mental Health Crisis? The Alarming Reality!
2025-03-25
Author: Ming
In recent years, the advancement of artificial intelligence, particularly in the realm of chatbots, has ignited a heated debate about their impact on mental health. As technology evolves, the lines blurring between social interaction and AI companionship have raised significant concerns. While social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok have been scrutinized for their effects on user well-being, emerging evidence suggests chatbots could pose similar—or even greater—risks.
In 2023, a pronouncement from the U.S. Surgeon General underscored the potential dangers of social networks to the mental health of younger populations. However, this advisory highlights the ongoing struggle to understand social media's multifaceted effects, with various studies producing conflicting results on their influence on overall well-being. Efforts by lawmakers to impose restrictions on social media use have met with challenges, as many proposals face legal roadblocks grounded in First Amendment protections.
The situation has taken a more troubling turn with incidents like the tragic case of a 14-year-old boy in Florida, whose family filed a lawsuit against a chatbot company, Character.ai, alleging the bot contributed to his suicidal ideation. Such stories hint at an unsettling pattern as millions turn to chatbots for emotional and even sexual connections.
One of the core concerns about chatbots is their designed intention to engage users deeply, often leading to heightened emotional attachments. Unlike the impersonal nature of traditional social media, these AI-driven companions offer personalized interactions, tailor-made responses, and a semblance of real human connection. However, this raises an important question: How does prolonged interaction with AI impact users’ social lives and mental health?
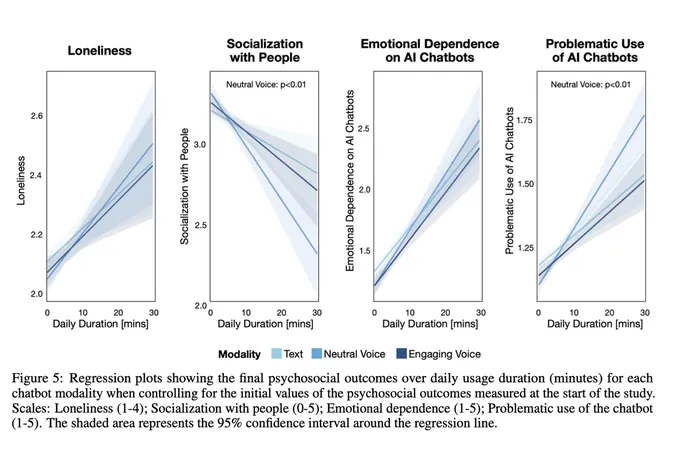
Recent studies conducted by researchers at the MIT Media Lab and OpenAI have attempted to quantify these effects. An analysis of over four million ChatGPT conversations revealed patterns suggesting a correlation between intense chatbot use and feelings of loneliness. Another study involving nearly 1,000 participants highlighted a troubling trend: users who engaged deeply with ChatGPT reported increased emotional dependence and a decline in real-world social interactions.
The researchers noted a critical finding: individuals seeking emotional connections are often those feeling lonelier and inclined to spend more time engaging with chatbots. While this observation does not conclude that chatbots are directly causing loneliness, it paints a concerning picture of users potentially retreating into synthetic relationships at the expense of real human connections.
Companies designing chatbots primarily marketed as emotional companions—like Replika and Nomi—are particularly noteworthy as they offer users personalized experiences that mimic romantic engagements. They leverage subscription models to keep users invested in maintaining these digital bonds, which could inadvertently foster dependency and feelings of isolation when real-world interactions diminish.
Despite the promise of AI chatbots to assist in alleviating loneliness and providing emotional support, researchers stress the importance of responsible development. Platforms are encouraged to implement early warning systems to identify unhealthy usage patterns and to find ways to organically nudge users towards balancing their AI interactions with real-life relationships.
As regulations evolve to confront the challenges posed by social media, they must now extend to the AI landscape, anticipating the growing role of chatbots in our social fabrics. Lawmakers should focus on preventing exploitative practices that could target vulnerable individuals suffering from loneliness.
The potential benefits of chatbots in enhancing emotional support cannot be overstated—particularly as many individuals lack access to adequate mental health resources. However, it is crucial for developers to accept a shared responsibility for the mental well-being of their users. Just as social platforms failed to recognize the negative outcomes stemming from their services, the AI community must ensure that it does better, proactively fostering healthy interactions that prioritize user welfare.
In summation, while chatbots hold promise as life-enhancing tools, their impact on mental health warrants serious and immediate scrutiny. Are we ensuring that these AI companions truly serve us, or are we paving the way for a new kind of isolation? The time to act is now—before a new crisis unfolds.





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)