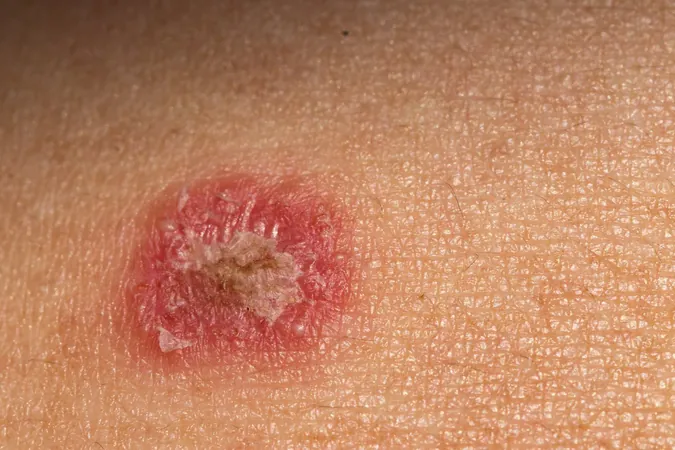
Alarm Raised: New Sexually Transmitted Ringworm Fungus Escalates in New York City!
2024-11-05
Author: Wei
New York City, known for its vibrant culture and fast-paced lifestyle, is now facing an unexpected health scare. Recent research published in a respected medical journal reveals the emergence of a sexually transmitted ringworm fungus that has already infected five individuals in the city this year. This disturbing development has raised concerns among health professionals and the LGBTQ+ community alike.
Among the more than 40 types of fungi responsible for causing ringworm— a misnomer that refers to rather annoying fungal infections characterized by ring-like rashes on the skin—one particular strain has caught the attention of dermatologists: Trichophyton mentagrophytes ITS genotype VII, or TMVII. Unlike its counterparts, TMVII spreads predominantly through close sexual contact, which is a rarity for ringworm infections.
The first documented case of TMVII in the United States was reported earlier this June by researchers at New York University Langone Health, who discovered that prior occurrences were primarily confined to Europe and Asia. Following this groundbreaking case, additional reports revealed four more infections between April and July in the city. While all five cases have been treated successfully, some patients endured multiple rounds of antifungal therapies.
The researchers have emphasized the urgency for health care providers to recognize TMVII as a sexually transmitted pathogen that can cause lesions on various body parts, including genital areas, buttocks, and face. Among the infected individuals, all five were cisgender men, with two engaging in sexual contact with each other, one being a sex worker. Previous clusters of infections have predominantly affected the same demographic, although heterosexual men and women have also been reported as cases.
TMVII is believed to have first emerged in Southeast Asia, where its spread was likely facilitated by interactions with infected sex workers. After establishing itself in Europe, experts caution that the fungus could be becoming endemic in the U.S. Based on reported cases without clear transmission links, the potential for local transmission in NYC and beyond is a growing concern.
Dr. Avrom Caplan, an investigator and specialist in autoimmune skin disorders, elaborated on the situation: “While we have confirmed only a handful of cases in the U.S., it is prudent to consider the chances of local spread given the situation in Europe. The potential for TMVII to escalate into a more widespread issue cannot be overlooked.”
In light of this alarming development, Caplan and his team are advocating for heightened awareness among medical professionals and the public. They urge anyone displaying symptoms of a fungal infection to avoid close contact with others, stressing that early diagnosis and preventive health measures are crucial.
“To combat the threat of TMVII effectively, clinicians and patients need to understand this new infection, which requires antifungal treatment and could be mistaken for other dermatologic issues,” Caplan stated. “Awareness and preventive measures are especially vital in sexual health clinics, catering to populations at higher risk.”
Adding to the growing concerns, health researchers have also reported cases of another emerging fungus, Trichophyton indotineae, in New York, which potentially leads to more severe infections and may resist standard antifungal treatments.
As NYCs battle against these emerging health threats intensifies, vigilance in sexual health practices and prompt medical responses are imperative. Stay aware and informed—your health might depend on it!





 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)