
A Comet More Brilliant than Venus: Don’t Miss This Once-in-a-Lifetime Celestial Spectacle Next Week!
2025-01-08
Author: Ling
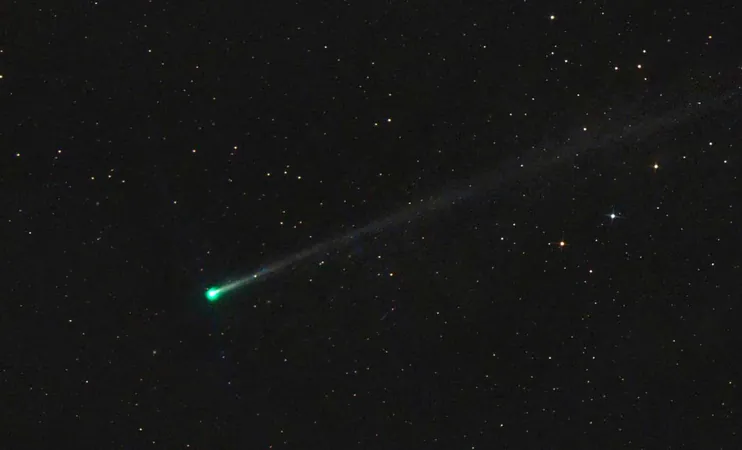
Next week, skywatchers are in for an extraordinary treat as Comet C/2024 G3 (ATLAS) nears the Sun, promising an unforgettable astronomical event. This dazzling "sun-grazer" is expected to reach a peak brightness of magnitude -6.1, potentially outshining Venus, the second-brightest object in our night sky. This celestial display is a rare occurrence, making it a must-see for both amateur astronomers and seasoned stargazers alike.
What is Comet C/2024 G3 (ATLAS)?
Comet C/2024 G3 is a long-period comet with a daunting orbital period of approximately 135,000 years—meaning it last graced our skies during the Ice Age! Its perilous flight path brings it extremely close to the Sun, drastically increasing the risks associated with its solar approach. As a sun-grazer, it faces disintegration from intense solar radiation, creating both excitement and apprehension about its visibility.
Why Is This Comet So Bright?
The comet's predicted brightness is fueled by its close approaching distance to the Sun and the volatile nature of its icy nucleus. As it nears the Sun, solar energy vaporizes its icy core, releasing dust and gas that form a glowing coma and an impressive tail that can extend millions of kilometers into space. The result is a brilliant spectacle that shines in the night sky, catching the eye of countless observers.
However, comets often display unpredictable behavior. The same solar forces elevating its brightness could also spell disaster, leading to its disintegration. While C/2024 G3 has thus far met or exceeded brightness expectations, the uncertainty surrounding its fate only adds to the thrill of witnessing this celestial phenomenon.
Challenges in Observing C/2024 G3
While the comet is set to be incredibly bright, viewing it won’t be easy. Peaking on January 13, 2025, its orbital location will place it dangerously close to Sun's glare, making visibility a significant challenge without specialized equipment.
Viewing Tips:
- **Southern Hemisphere Advantage:** Stargazers in places like Johannesburg, Cape Town, and São Paulo will have the best chances to catch a glimpse, as the comet will pass nearly overhead. Meanwhile, observers in the Northern Hemisphere will struggle due to positional challenges and solar interference.
- **Optimal Viewing Time:** The best chance to see the comet will be around January 20, 2025, after it has moved slightly away from the Sun’s direct glare. While it will be fainter, it will still be visible during twilight hours.
- **Essential Gear:** Binoculars or telescopes fitted with solar filters are recommended for safe and effective viewing, particularly during daylight. These instruments enhance visibility, revealing the comet’s intricate coma and tail.
Observers should also be mindful of external factors such as weather and light pollution, which can obscure the view. Finding dark-sky locations away from urban lights will enhance the chances of a successful observation.
Comparisons with Other Comets
C/2024 G3 is garnering attention for its tremendous brightness and potential viewing advantages over other recent comets like C/2023 A3 (Tsuchinshan-ATLAS). Here’s how C/2024 G3 stands out:
- **Brightness:** It is predicted to reach brightness levels of magnitude -6.1, significantly more luminous than C/2023 A3's max of -4.
- **Visibility:** Its trajectory is more favorable for the Southern Hemisphere, which offers better visibility compared to C/2023 A3.
- **Rare Orbital Period:** With its awe-inspiring 135,000-year orbit, C/2024 G3 is a unique visitor compared to others with much shorter cycles.
The Comet’s Perilous Journey
As the comet approaches the Sun, it faces tremendous risks; the extreme heat could shatter its icy nucleus. Nonetheless, C/2024 G3 appears to possess remarkable resilience, having survived its last solar close encounter millennia ago. Should it survive, it will display a stunning vista of cosmic endurance with a revitalized coma and tail. Conversely, if it disintegrates, it joins a long lineage of sun-grazing comets that succumbed to the Sun’s immense might.
Why This Matters
Comets like C/2024 G3 do more than provide awe-inspiring spectacles; they act as celestial time capsules, revealing insights into the early solar system. By studying their composition, scientists can glean information about the building blocks of planets and other celestial bodies.
Observations of sun-grazing comets also allow us to learn more about the Sun itself. The interactions between the comet’s materials and solar radiation yield valuable data about solar phenomena, enhancing our understanding of space weather and its effects on Earth.
In conclusion, whether Comet C/2024 G3 delivers a vibrant display or succumbs to solar fury, its odyssey embodies the captivating and ever-evolving characteristics of our solar system. Don’t miss out on the chance to witness this spectacular celestial event!


 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)