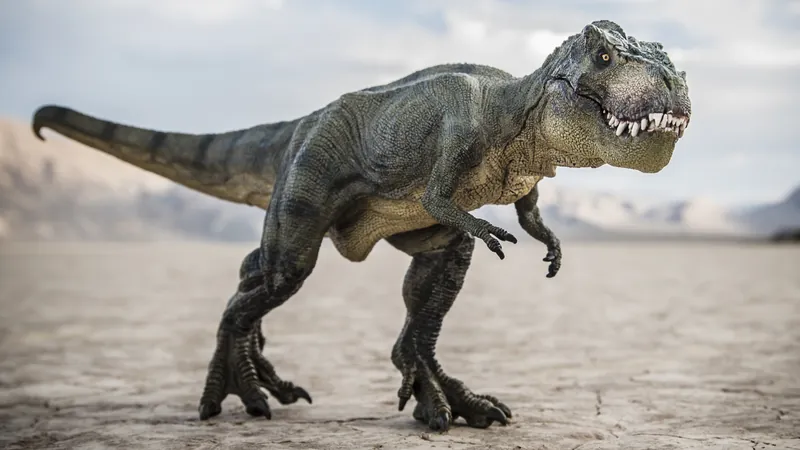

Unveiling the Origins of T. rex: Did This Ferocious Giant Evolve in North America?
2025-05-07
Author: Jacob
The Origins of T. rex Shrouded in Mystery
A recent groundbreaking study might rewrite the history of one of the most fearsome creatures to ever roam the Earth: the Tyrannosaurus rex. Contrary to long-held beliefs that T. rex's ancestors originated in Asia and traveled to North America, fresh evidence points to the possibility that this iconic predator actually evolved in North America itself.
A Journey Across Ancient Lands
Published in the journal Royal Society Open Science, the study suggests that while T. rex's as-yet-undiscovered direct ancestors likely started in Asia, they made their way to what is now North America more than 70 million years ago, specifically during a time when lower sea levels created a land bridge between the continents.
A Colossal Predator Across the Ages
Living from about 67 to 66 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period, T. rex was not just a massive predator but a local ruler, measuring up to 12.5 feet tall at the hips and stretching 41 feet long. Most fossils have been unearthed in Montana and South Dakota, areas once part of an island continent called Laramidia that spanned from modern-day Alaska down to Mexico.
The Great Debate Among Paleontologists
The debate over T. rex's origins has been contentious among paleontologists. A 2016 study indicated a closer anatomical relationship between T. rex and Asian tyrannosaurids than their North American cousins. The latest research builds on these findings and posits that T. rex's evolutionary journey had its roots in North America.
Cassius Morrison, the lead author and a doctoral researcher at University College London, stresses the importance of this discovery: "Our modeling indicates that the ancestors of T. rex likely arrived in North America through the Bering Strait, showcasing their migration from Asia."
Tracking the Genetic Journey
By analyzing the geographic distribution of tyrannosaurid fossils and their evolutionary relationships, the researchers believe that T. rex's ancestor roamed both Asia and North America, migrating roughly 72 million years ago, during the Late Campanian to Early Maastrichtian.
The Immigrant Giant of America
Steve Brusatte, a notable paleontologist at the University of Edinburgh, emphasized the irony of T. rex's status as the quintessential American dinosaur: "It was big, bold, and ferocious, reigning supreme during the final stages of the Cretaceous, but it was, in fact, an immigrant from Asia."
Growing Up Gigantic: How Climate Influenced Dinosaur Size
The researchers also delved into how both T. rex and its relatives, the megaraptors—which were equally colossal and could reach up to 33 feet—achieved such massive sizes. They found that climatic shifts during the Cretaceous Thermal Maximum, caused by surges in atmospheric CO2 and methane from volcanic activity, played a significant role. The resulting warm climate paved the way for these giants to thrive after other large dinosaur species went extinct.
Charlie Scherer, a co-author of the study, noted, "By the end of the era of dinosaurs, tyrannosaurs emerged as the largest due to the ecological niches opened up by climate changes. The extinction of larger carcharodontosaurids allowed tyrannosaurs to grow unchallenged."
Climate's Role in Dinosaur Domination
In essence, this study illustrates how even the most dominant creatures—like T. rex—were influenced by the climate. Brusatte concluded, "The rise of tyrannosaurs was not merely a matter of chance. Their evolution into the titans of the Cretaceous was closely tied to changing environmental conditions, highlighting the intricate link between climate and the evolution of these majestic dinosaurs."








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)