Unveiling the Mysteries of a Pulsar Planet's Unique Atmosphere
2025-09-15
Author: Amelia
A Shocking Discovery in the Cosmos
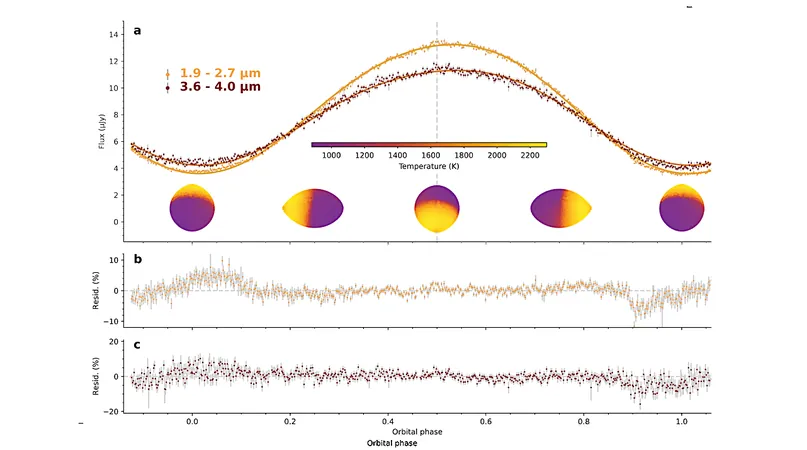
Astronomers have unearthed a fascinating gem in the universe—PSR J2322-2650b, a massive planet orbiting a pulsar that bears striking similarities to a 'hot Jupiter' exoplanet. With a minimum density of 1.8 g/cm³ and a sizzling equilibrium temperature of around 1900 K, this celestial body is challenging everything we thought we knew about planetary atmospheres.
Exploring the Atmosphere with JWST
Thanks to the powerful James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), researchers are now able to observe the planet's emission spectrum throughout its entire orbit. In a stunning twist, the findings reveal an atmosphere brimming with molecular carbon compounds, such as C3 and C2, accompanied by fierce westward winds that sweep across the planet's skies.
A New Era of Exoplanetary Chemistry
The implications of these observations are profound, unveiling a previously uncharted territory in exoplanetary chemistry. PSR J2322-2650b showcases ultra-high carbon-to-oxygen (C/O) and carbon-to-nitrogen (C/N) ratios exceeding 100 and 10,000, respectively. This discovery heralds a new dynamic regime, characterized by rapid rotation and intense external irradiation.
A Challenge to Existing Theories
The extreme carbon enrichment also raises questions about the nature of ‘black widow’ companions—stellar remnants that were thought to contain a broader spectrum of elements due to their origin as stripped stellar cores. This revelation challenges existing theories and suggests a far more complex narrative about the life cycles of these peculiar celestial bodies.
What Lies Ahead for Astronomers?
As researchers delve deeper into the mysteries of PSR J2322-2650b and its distinctive atmosphere, the astronomical community is left buzzing with excitement. This discovery not only reshapes our understanding of planetary formation but could potentially unlock the secrets to life beyond our solar system.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)