
Unveiling Mars' Ancient Climate: What Rocks Reveal About Our Planet's Future
2025-06-13
Author: Liam
Mars: From Vibrant Waters to a Barren Wasteland
Mars, often dubbed the enigmatic Red Planet, has enthralled humanity for centuries with its otherworldly beauty and seemingly desolate terrain. Today, it stands as a cold, arid shell of what was once a thriving world, complete with rivers and lakes. Recent groundbreaking findings from NASA's Curiosity Rover shed light on what contributed to this climate shift, hinting at a history that could inform our understanding of climate change on Earth.
Siderite: The Key to Unlocking Mars' Secrets
In a recent episode of SETI Live, Dr. Ben Tutolo from the University of Calgary unveiled a remarkable insight: the unassuming iron carbonate mineral siderite is crucial in unraveling the atmospheric history of Mars. The discovery has significant implications, suggesting that Mars was once a much warmer and wetter place, requiring a thicker atmosphere filled with carbon dioxide — potentially a thousand times more than what we observe today.
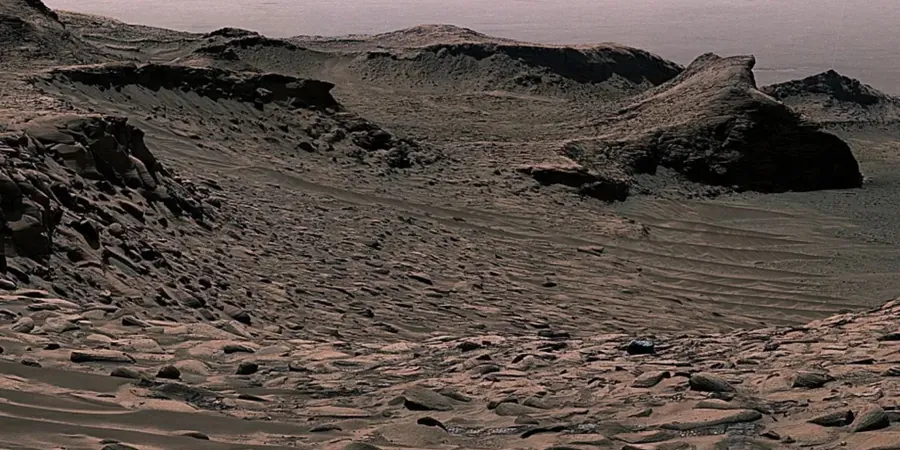
Curiosity's Remarkable Find in Gale Crater
Curiosity's voyage through Gale Crater has proven consistently revelatory. As it drilled into Mount Sharp's layers, the rover uncovered a treasure trove of siderite, with some samples boasting an astonishing 10.5% concentration. This significant mineral was completely overlooked by orbital surveys, underscoring the critical role of on-the-ground exploration by rovers.
A Window Into Carbon Sequestration
But why does siderite matter? On Earth, its cousin, calcite, forms the backbone of our long-term carbon cycle, effectively trapping carbon over time. On iron-rich Mars, siderite operates similarly, hinting at Mars’ ability to hold captured CO2 in its rocks. The presence of magnesium sulfate salts alongside siderite points to evaporation-driven processes that may have facilitated a massive carbon sequestration method, elucidating how Mars transitioned from a carbon-rich atmosphere to the dryness we see today.
A Cautionary Tale for Earth’s Climate Crisis
The implications of this discovery extend beyond the Martian surface. Dr. Tutolo draws parallels between Mars’ ancient climate and our current Earthly plight, as scientists explore carbon capture methods to combat climate change. The Martian experience serves as a stark reminder of just how fragile planetary climates can be. A basic imbalance in CO2 levels, sustained over time, can lead to drastic consequences, as evidenced by Mars’ climate shift.
Searching for Life: Mars’ Potential Habitability
The findings regarding siderite also fuel our quest for extraterrestrial life. If Mars held warm, wet conditions for a billion years, it opens up a crucial window for understanding potential habitability. Future missions targeting this interval might hold the keys to discovering life’s origins beyond Earth.
Rethinking Habitability in the Universe
Moreover, this discovery challenges our assumptions about habitability zones. If Mars, which appears too distant from the sun to support life, once had conditions ripe for water, it prompts a reevaluation of what we consider acceptable parameters for life-sustaining environments.
A Technological Triumph
Curiosity's success can be attributed to its advanced instruments, particularly the ChemMin X-ray diffraction tool, which enabled precise mineral analysis. This technology played a pivotal role in revealing the abundance and purity of siderite, showcasing how far we have come in our quest for knowledge about our neighboring planet.
The tale of Mars is not merely an account of a barren world; it’s a potent narrative about the delicate balance of planetary climates — one that serves as a significant reminder for our own.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)