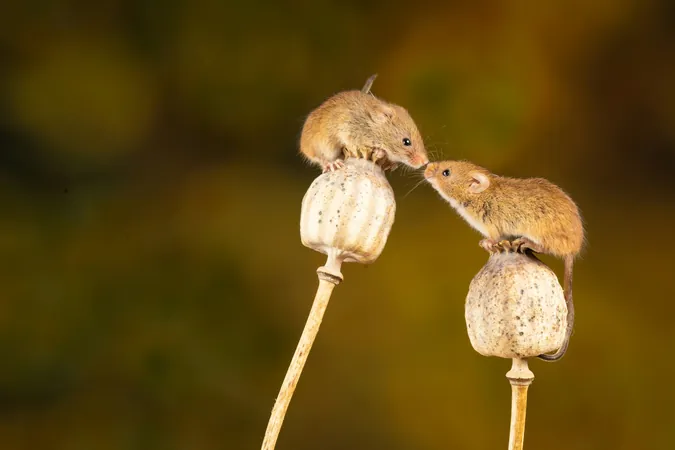

Unlocking the Secrets of Mouse Whiskers: More Than Just Touch!
2025-06-23
Author: Jacques
The Amazing Whiskers of Mice
Have you ever fumbled around in the dark, desperately searching for your lost keys? While you might feel around with your hands, a mouse has a far more sophisticated tool at its disposal—its whiskers!
These long, sensitive hairs, known as vibrissae, give mice the ability to navigate their surroundings with impressive accuracy. When a whisker brushes against an object, sensory neurons at the hair follicle spring into action, sending vital information to the mouse's brain about its environment.
Beyond Touch: A New Study Reveals Whiskers Can 'Listen'!
A groundbreaking study led by neuroscience Ph.D. candidate Ben Efron has unearthed an astonishing fact: mice may not only use their whiskers for touch but can also detect sounds made by these whiskers as they interact with surfaces!
This research is particularly beneficial for these nocturnal creatures, who thrive in the dark, burrowing through the unseen corners of our homes. By employing specialized muscles, mice can maneuver their whiskers in various patterns while running, turning, or examining objects—speeding up their whisker movements as their excitement increases.
Whiskers That Make Sounds: A Sensory Revolution!
The researchers noticed that when whiskers made contact with different surfaces, they produced faint sounds. Astonishingly, these sounds triggered brain activity even when the usual touch signal pathway was severed, indicating that mice have a unique ability to interpret sound as another form of sensory input. They were even trained to recognize surfaces based solely on the sounds their whiskers produced!
Rethinking Sensation: What This Means for Other Animals
Traditionally, scientists believed whiskers were purely for tactile exploration, but this revolutionary finding opens up questions: Do other whiskered animals share this ability? Could this dual functioning of whiskers lead to more nuanced environmental interpretations? Just like how you might sense the familiar jingle of your keys, mice may harness sound to guide their navigation.
A Hidden Symphony in Nature
Every species translates the world through its unique sensory capabilities. Mice's method of identifying objects via sound is reminiscent of echolocation used by bats and dolphins. These animals emit sounds that reflect off surfaces, allowing them to navigate and hunt even in complete darkness.
Remarkably, this adaptive survival mechanism evolves in response to predators, such as echolocating bats. Moths, for instance, have developed sound-defending mechanisms, showcasing nature’s resilience and ingenuity.
Even elephants communicate over long distances with low-frequency rumbles that are inaudible to the human ear—going beyond just vocal sounds to include seismic signals that resonate through the ground.
Why This Matters: Understanding a Hidden World
So, why should we care about these unseen worlds? As human activity increases, sound pollution disrupts these delicate communication systems among wildlife. From maritime noise affecting whales and dolphins to urban sound disrupting nesting birds, understanding these impacts is crucial for their protection.
Additionally, the innovative designs inspired by these natural phenomena could lead to new technologies—think of the ultrasonics in modern parking sensors, a technique that bats have mastered for millions of years!
As we delve deeper into the sensory capabilities of creatures like mice, we unlock secrets that promise to reshape our understanding of biology, technology, and conservation.








 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)