Unlocking the Secrets of Exoplanet Atmospheres: Insights from Titan and JWST's Hot Jupiters
2025-05-27
Author: William
A Breakthrough in Exoplanet Research
For years, the quest to understand the clouds and hazes in distant exoplanet atmospheres faced a significant hurdle: limitations in telescope sensitivity. However, thanks to recent advancements and particularly the groundbreaking capabilities of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), scientists are making strides in discerning these elusive atmospheric features.
Exploring the Potential of JWST
Our mission? To delve deep into the wealth of information JWST exoplanet spectra hold. We're developing a cutting-edge inversion technique that allows for the analysis of a diverse range of clouds and hazes found in various extraterrestrial atmospheres.
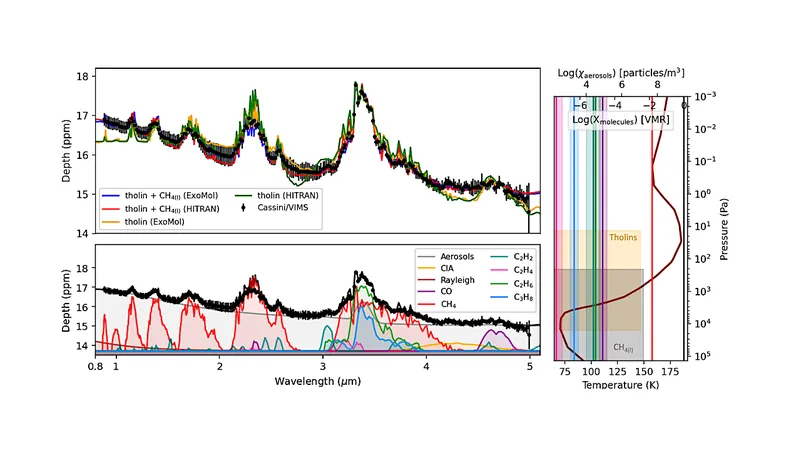
Innovative Methods for Atmospheric Retrievals
Utilizing the TauREx framework, we've created a versatile aerosol parameterization designed specifically for atmospheric retrievals. Our technique isn't just theoretical; it has been rigorously tested on data from Titan's Cassini occultations.
Decoding the Hot Jupiters
We're also applying our methods to interpret the latest JWST observations of hot Jupiters such as HAT-P-18 b, WASP-39 b, WASP-96 b, and WASP-107 b. Simultaneously, we run coordinated simulations to enhance our understanding and provide guidelines for future exoplanet studies.
Key Findings and Challenges Ahead
Our work has revealed essential atmospheric characteristics, including molecular abundance, thermal structure, and the properties of aerosols in these exoplanets. A critical observation underscores the importance of wide wavelength coverage to accurately identify clouds and hazes. This is crucial to avoid biases linked to unknown compositions and to overcome challenges presented by atmospheric chemical complexity.
The JWST Challenge: A New Frontier
While JWST opens doors to unprecedented discoveries, it comes with its own set of challenges. The limited capacity to cover simultaneous wavelengths from visible to mid-infrared still leaves gaps, and the natural variability of atmospheres between observations adds another layer of complexity. Factors such as changing observing conditions and stellar variability could affect the quality of the data.
The Future of Exoplanetary Atmosphere Studies
As we forge ahead in this thrilling field, the insights gleaned from both Titan and JWST will be pivotal in shaping our understanding of exoplanetary atmospheres. Each observation brings us closer to unraveling the mysteries of worlds beyond our own.









 Brasil (PT)
Brasil (PT)
 Canada (EN)
Canada (EN)
 Chile (ES)
Chile (ES)
 Česko (CS)
Česko (CS)
 대한민국 (KO)
대한민국 (KO)
 España (ES)
España (ES)
 France (FR)
France (FR)
 Hong Kong (EN)
Hong Kong (EN)
 Italia (IT)
Italia (IT)
 日本 (JA)
日本 (JA)
 Magyarország (HU)
Magyarország (HU)
 Norge (NO)
Norge (NO)
 Polska (PL)
Polska (PL)
 Schweiz (DE)
Schweiz (DE)
 Singapore (EN)
Singapore (EN)
 Sverige (SV)
Sverige (SV)
 Suomi (FI)
Suomi (FI)
 Türkiye (TR)
Türkiye (TR)
 الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)
الإمارات العربية المتحدة (AR)